Decadron dosages: 8 mg, 4 mg, 1 mg, 0.5 mg
Decadron packs: 10 pills, 20 pills, 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

1 mg decadron purchase with mastercard
Amphoric breath sound: It is a metallic high quality bronchial breath sound-high-pitched tazorac 005 acne decadron 8 mg for sale, loud and resonant acne jawline decadron 0.5 mg cheap without a prescription. Like tubular breath sound long and well-preserved expiration, (Inspiration:Expiration = 1:1). Like vesicular breath sound lack of silent phase between inspiration and expiration. They are soft and low-pitched, like vesicular breath sound and harsh, and loud like tubular breath sound. The peculiar bronchovesicular breath sound is as a end result of of peculiar transmission of the sound: First it produces turbulent move in large and central airways. Then it crosses a skinny mantle of alveolar air before reaching to chest piece of stethoscope. Adventitious Sounds these sounds are normally absent in respiratory cycle, but turns into superimposed on underlying bronchial or vesicular breath sounds when the lung will be diseased z these sounds may be: Discontinuous (if lasting <250 msec) Continuous (if lasting >250 msec). Mechanism of manufacturing of adventitious sound: Adventitious sounds are produced by vibration of respiratory structures and pleura. The mechanism is Bernoulli precept: If the water flows through narrow tube, then it produces suckling impact, which in flip draws-in air through holes. Discontinuous adventitious lung sounds: z They are (< 250 msec) brief z They are largely inspiratory, may happen in expiratory z They are commonly crackles. Production of Wheeze When luminal narrowing occurs, air should move with greater velocity through the constricted regions to keep up constant flow rate. According to Bernoulli principle, increased air velocity leads to lower in air stress, thus allowing exterior stress to further collapse the airway. The underlying breath sound during crackles Production or presence of type of breath sounds during crackles depends upon sort of crackles. Fluid-filled alveoli: Produces late inspiratory crackles and bronchial breath sound Fluid-filled interstitum: Produces late inspiratory crackles and bronchial breath sound Scarring of interstitum: Produces late inspiratory crackles and vesicular breath sound. Breath sound Vesicular breath sound No crackles Normal lung Late crackles Scarring interstitium Bronchial breath sound No crackles Collapsed alveoli Late crackles Fluid filled pus fluid serum 244 Clinical Methods and Interpretation in Medicine Mechanism of production of crackles: z Early and mid-inspiratory crackles: Coarse sounds produced by bubbling of air by way of the secretions in giant and medium size bronchi. These secretions are changed with coughing They are principally heard over central a half of chest anteriorly and posteriorly. Brochiectatic crackles are produced by circulate of air through secretions accumulated in dilated wall produced by destruction of musculoelastic frame work. This high interstitial strain behind them is due to, scarring of interstitium or fluid, pus or blood in interstitial areas (pulmonary edema, pneumonia, pulmonary hemorrhage). Regional variations of late inspiratory crackles: In posterior lung bases-due to area of high interstitial strain, gravity can easily collapse the bronchi-producing late inspiratory crackles. Late inspiratory crackles could happen in early and mid inspiratory interval, however the hallmark is it must be current till late inspiration. Late inspiratory crackles happen in: z Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis z Asbestosis z Sarcoidosis (5�20%). These are not often current in: Granulomatous ailments z Tuberculosis z Allergic alveolitis z Eosinophilic granuloma. Areas of late inspiratory crackles: z Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Lower lobe location and subpleural searing z Sarcoidosis: Upper lobe location z Asbestosis: At the bases-first centrally, adopted by posterolaterally. Correlation with illness severity: z Number of crackles: Correlates with severity of asbestosis z Absence of crackles: Eliminates prognosis of interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. Correlation with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: z In milder case: Crackles are late inspiratory and gravity dependent limited to bases in upright patients z As the disease progresses: It turns into pan-inspiratory with predominant late inspiratory-present regardless of change in posture eventually they attain apical area. Importance of late expiratory crackles: Number of expiratory crackles correlates with reduction in diffusion capability. Continuous Adventitious Sound Rhonchi: Musical sound produced by move of air by way of narrowed bronchi-due to edema and/or mucus plug. Monophonic and polyphonic wheeze: z Monophonic wheeze: Contains single or multiple tones starting and ending at totally different instances this can be produced by a tumor virtually fully obstructing bronchi. This fluttering relies upon upon: z the mass z Elasticity of the bronchial wall z Tightness of narrowing z Rate of gasoline move via it. Physical precept behind wheeze productions: the Bernoulli principle: It suggests-local drop in intra-airway pressure when airflow at excessive velocity through it. Respiratory System 247 As the speed of airflow might be increased, intra-airway stress decreases, eventually drop in strain might be severe sufficient to break down the airway. Again collapsed airway reduces the airflow; airway reopens, fluttering cycles starts-repeating it repeatedly. Presence of wheezing rule in or not bronchial narrowing: z In normal people pressured expiratory maneuver produces wheezing. So it has very low specificity and low sensitivity in bronchial asthma z Weak expiratory circulate stays totally silent whereas passing through fairly narrowed bronchi. Underlying breath sound in asthmatic patient Since breath sound relies upon upon degree of narrowing of bronchi, so following kinds of breath sounds can be heard: z Increase in frequency of underlying breath sounds-it is the earliest manifestations of bronchospasm even before the looks of wheeze z As the airway becomes narrower, breath sound turn into soften z Opposite impact happens during bronchodilator therapy Respiratory System z 249 Softening of breath sounds may be the earliest manifestation of bronchoprovocation. The course of status asthmaticus based mostly on auscultation: z In gentle asthma: Site of obstruction within the central airways Bronchial wall fluttering produces random monomorphic wheezes transmitted upwards (to the mouth) and downward (to the chest wall). Subsequently: z Airway fluttering strikes to peripheral airways z Airflow is so slow, that it fails to generate vibrations. Relationship with pulsus paradoxus Pulsus paradoxus has a direct relation with hypercapnia in kids with status asthmaticus, so acts as indirect monitor of hypercapnia. Stridor: z High pitched z Inspiratory z It indicates higher airway obstruction z Louder over the neck. This layer is lubricated by thin film of fluid, so that in normal respiration the pleural surfaces glide on one another silently z During pleural inflammation, pleural floor are lined by fibrin and inflammatory/neoplastic cells, in consequence the roughened pleural surfaces rub towards one another during respiration producing grating sound-pleural rub z As the fluid accumulates in the pleural house, pleural surfaces are separated, pleural rub disappear So pleural rub in pathgnomonic of pleural inflammation. Most frequent causes of pleural rub: z Inflammation: Infective-pneumococcal, staphylococcal, gram �ve bacteria Noninfective-collagen vascular disease. Type of transmitted voice sounds are: z Bronchophony: that is heard over the chest areas remote from both bronchi or larynx-but as clear heard as over central bronchi or larynx z Pectoriloquy: the sound heard is clear and intelligible phrases over the chest within the form of either: Whispering (whispering pectoriloquy) Speaking (spoken pectoriloquy). Significance of this maneuver: It suspects irregular sound transmission alongside the tracheobronchial tree across the lungs when suspecting consolidation. The alveolar air acts as low-pass filter, eliminating excessive frequency sounds (>3000 Hz) and most of low frequency sounds (100�300 Hz) attain the chest wall. This filter also eliminates high frequency components of vowels so known as formants. Because recognition of vowels is important for comprehension of words, elimination of formants by the normal lung, hence voice sounds heard on the chest wall is low pitched, unintelligible, mumbles. But in case of consolidation-solid lung (fluid or solid) can transmit greater frequencies, so transmitted vowels become louder, clear and intelligible. Mechanism of E to A change: Consolidation extending from chest wall to tracheobronchial tree produce E to A change. The most typical causes of consolidation: z Filling of alveoli with: Pus Fluid Blood. The exception is-patient with collapsed bronchi or obstructed bronchi nonetheless manages to transmit excessive frequency sound by way of lung parenchyma immediately. Transformation of E to A in vocal resonance in consolidated lung: z E is a combination of high and low frequencies-high frequencies are 2000 to 3500 Hz and low frequencies are a hundred to 400 Hz range A is a mixture of excessive and low frequencies-low frequencies are higher than the low frequencies of E (600 Hz). Disease Vesicular Late-inspiratory crackles at bases (resolved with deep breath) Late inspiratory crackles Late inspiratory crackles Mid inspiratory crackles Early inspiratory crackles Rub above effusion Absence Trachea Fremitus Percussion notice Breath sound Adventitious sound Vocal resonance � Normal Midline Normal Resonant � Consolidation (pneumonia hemorrhage) Bronchovesicular Vesicular Vesicular Absent over effusion bronchial above effusion Midline Increased Woody dull Bronchial (tubular) Increased � Pulmonary fibrosis Midline Increased Dull Absent Absent Absent Egophony above effusion absent above effusion Contd.
Cissus Quadrangularis. Decadron.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Cissus Quadrangularis?
- Obesity and weight loss, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and high cholesterol, bone fractures, osteoporosis, scurvy, cancer, upset stomach, hemorrhoids, stomach ulcer, menstrual discomfort, asthma, malaria, pain, and body building.
- How does Cissus Quadrangularis work?
- Dosing considerations for Cissus Quadrangularis.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=97110
Purchase decadron 1 mg otc
Thus a affected person with pseudobulbar palsy or an oesophageal fistula or Enteral diet Oral route It is crucial to provide heat, appetising food in hospital, and elderly/infirm sufferers may need help to take their meals and the help of relations may be useful acne rosacea pictures 0.5 mg decadron purchase amex. It is against this basic background of nutritional care that the need for synthetic nutritional help should be thought-about skin care 08 cheap decadron 0.5 mg without prescription. Encouraging patients to eat small amounts frequently or to sip an oral complement between meals might help overcome this symptom. Oral supplements must be palatable and can be found in cartons of roughly 250 mL (approximately 250 kcal and 10 g of protein). They are often available in a selection of flavours and could additionally be more palatable if chilled. Most sufferers handle to eat one or two cartons per day, but fatigue with such dietary supplements is commonplace and leads to decreased efficacy. It could be extremely tough to watch the adequacy of enteral feeding, notably within the presence of diarrhoea and/or vomiting. Excessive infusion of nasogastric feed might trigger marked stomach bloating, leading to splinting of the diaphragm and impaired respiratory perform. Fine-bore tubes must be flushed thoroughly if relaxation periods are employed as they block shortly if feed is left in them. Examples include a fine-bore nasogastric tube inserted wrongly into the respiratory tract (or even via the cribriform plate into the anterior cranial fossa), early accidental removal of a jejunostomy tube with intraperitoneal leakage, or peritubal leakage with resultant intraperitoneal contamination. The fixation of the jejunal loop to the stomach wall, required to minimise the risk of intraperitoneal leakage associated with feeding jejunostomy, may in flip enhance the danger of small bowel volvulus, though that is extraordinarily uncommon. Enteral feeding in critically unwell patients, normally on inotropic help, who may already have a level of splanchnic hypoperfusion, has not often been related to precipitating acute extensive mesenteric infarction, possibly because of the elevated metabolic necessities of the gastrointestinal tract in response to the delivery of nutrients (nonocclusive mesenteric ischaemia). Boil 150�200 mL water; to this add the rice flour paste, stirring continuously to forestall lumps. Jejunostomy is most well-liked in cases where the stomach could also be required for surgical reconstruction of the proximal lesion. Feeding jejunostomy tubes can be inserted on the time of laparotomy if the surgeon anticipates that extended nutritional help shall be wanted postoperatively. The bowel ought to be securely anchored to the parietal peritoneum circumferentially around the tube (see later). As a rule, 2000�3000 kcal ought to be provided, of which carbohydrates and fats present 30�40% each. Enteral feeds may be prepared by the hospital kitchen or could additionally be out there commercially based on the calorie and protein, carbohydrate and fats requirement. Fine-bore nasogastric/nasojejunal/gastrostomy/jejunostomy tubes require a feed that might be a homogeneous easy emulsion and solely commercially obtainable proprietary preparations satisfy these necessities. In circumstances of a high-output stoma, or proximal small bowel Complications of enteral nutrition Complications of enteral nutrition could also be a minimum of as frequent as with parenteral vitamin and can be equally life-threatening. Diarrhoea is extra widespread with nasogastric than with nasojejunal feeding and can be managed by reducing the rate of infusion and by avoiding broad spectrum antibiotic remedy. Vomiting can be managed by decreasing the rate of feeding and by the use of prokinetic medication corresponding to metoclopramide or erythromycin. Monitoring of fluid and electrolyte balance is essential, a minimum of within the acute part Methods of offering nutritional assist � forty five fistula, parenteral feeding is sustained till the fistula has closed spontaneously or has been closed surgically. Most pharmacies have three or four commonplace regimens obtainable for compounding, based on necessities. The solutions comprise fastened quantities of power and nitrogen, and typically present 1400�2400 kcal (50% glucose, 50% lipid) and 10�14 g nitrogen. Trace elements and nutritional vitamins may additionally be included, and the calls for created by infection and extreme loss can thus be met. Thus, they have to be infused comparatively slowly right into a vein with a excessive blood move to forestall chemically induced thrombophlebitis and secondary venous thrombosis. The catheter tip is usually sited, utilizing radiological steerage, at the junction of the superior vena cava and right atrium, because the blood move is maximal at that time. For longer-term feeding, catheters are tunnelled subcutaneously to reduce the chance of infection. For very long-term (including home) parenteral feeding a Hickman catheter is used; this kind of silastic catheter has a Dacron cuff, which secures it in the subcutaneous fats. With good care, a accurately positioned Hickman catheter can remain in place for a couple of years with out an infection or occlusion. Ultrasound guidance ought to at all times be used for catheter placement, because it permits such problems to be averted almost utterly. Incorrect catheter positioning is excluded by taking a chest x-ray previous to commencing infusion. The telltale signs are redness and tenderness over the cannulated vein, together with swelling of the whole limb and engorgement of collateral veins if the thrombosis is extra proximal. Occasionally, a superior mediastinal syndrome develops in patients with superior vena cava thrombosis. If main vessel occlusion is suspected, the prognosis is confirmed by venography and anticoagulation is commenced with heparin. If vascular entry must be maintained, an attempt may be made to lyse the clot with urokinase or plasminogen activator given via the catheter in addition to systemic anticoagulation. There is a physiological upper limit to the amount of glucose that could be oxidised (4 mg/kg/min) and extended glucose infusion in extra of this price might lead to hyperglycaemia and fatty infiltration of the liver with disordered liver perform. However, severe and progressive abnormalities and, specifically, biochemical or clinical jaundice should result in a prompt re-evaluation of the feeding routine. Excessive administration of glucose may also irritate respiratory failure as a consequence of the necessity to get rid of larger amounts of carbon dioxide consequent upon increased carbohydrate oxidation. Intolerance of glucose is especially doubtless in sepsis and important sickness because of insulin resistance. Hyperglycaemia could require a reduction of the glucose load, concomitant infusion of insulin by way of a separate pump, or each. Catheter infections are entirely avoidable and are virtually all the time the results of poor line care, with infection often launched via the catheter hub as a end result of deficient aseptic technique. The insertion website have to be protected with an occlusive dressing and ought to be cleansed on alternate days with an antiseptic agent. The line should only be used for infusion of vitamins and by no means for taking or giving blood, or administering medication. If the adjustments are marked and progressive, the general substrate load ought to be lowered and discontinuation of parenteral vitamin considered. Monitoring of nutritional help Patients receiving nutritional assist are monitored to detect deficiency states, assess the adequacy of power and protein provision and anticipate complications. Patients receiving enteral feeding require much less intensive monitoring, however are prone to the same metabolic issues as those fed intravenously.
0.5 mg decadron buy mastercard
After start skin care names discount decadron 4 mg visa, adult haemoglobin (Hb A) skin care 70 1 mg decadron best, which accommodates two alpha and two beta chains (22), quickly will increase from roughly 10% of all haemoglobin at start to approximately 98% during infancy. White blood cells and lymphocytes appear within the peripheral blood late in the first trimester. The white cell depend is low early in pregnancy-approximately 1 Ч 109/L at week 25-but reaches roughly 8 Ч 109/L at term. Immune globulins are produced after the first trimester, and the presence of an an infection in fetal life may be inferred by finding disease-specific immunoglobulin M (IgM) in twine blood. The Wolffian is the male accessory duct system and the Mьllerian is the feminine genital system. The gonads are populated by germ cells which have migrated from the primitive yolk sac, and these are juxtaposed to the higher part of the genital ducts. The kidneys kind from metanephric tissue which is invaded by an outpouching of the metanephric duct (the ureteric bud). As with different organs such as the lung and liver, repeated branchings occur till the final models of function are achieved (in this case the nephron, there being 1 million or extra in every kidney). At the tip of the primary trimester, the fetal kidney is in a position to filter and reabsorb urine, however concentrating capability and acidification is poorly developed until after start. The bladder forms when the urorectal septum descends and separates the bladder in front from the rectum/anal canal behind. The urethra is fashioned from grooves which appear on the vulva and shut over; the female lacks the penile urethra, the folds remaining open to present the labia minora. Glomerular filtration and tubular absorption rates are considerably lower than within the grownup on a surface area foundation. The gastrointestinal system develops from the elongation and folding of the primitive foregut, midgut and hindgut. The abdominal bulge seen in the embryo represents the midgut, which is just too large to be accommodated within the belly cavity and herniates into the umbilical cord from weeks 8 to 12. Muscle tissue develops across the endodermal epithelium, and anatomical developments (formation of the appendix and caecum, rotation of the gut) happen in the embryonic period. The fetus swallows amniotic fluid from the top of the primary trimester; the quantity reaches 50 mL or extra per hour in late being pregnant. Communication with the allantois ceases at approximately weeks 7 to eight by the formation of the urorectal septum. This ought to break down by the tip of the 10th week; failure to accomplish that offers rise to the situation of imperforate anus. There are two types of lining cells: squamous and granular pneumatocytes; the latter, which seem at in regards to the 6th month, produce surfactant that lowers floor tension in the alveolus. Primitive respiration actions could be noticed by ultrasound as early as the 12th week of fetal life; they turn into progressively extra frequent, deep and coordinated as gestation advances. The frequency of chest movement is roughly 50 per minute and such activity occupies approximately 50% of any noticed time period in late pregnancy. The thyroid, parathyroid and thymus glands are all derived from the pharyngeal pouches over weeks 3 to 5; perform often commences late within the first trimester. The liver bud, which additionally forms the gall bladder, arises from the primary part of the longer term duodenum. The liver is a relatively massive organ in fetal life, especially in the course of the period of haematopoiesis. Gluconeogenesis happens from the tenth week and glycogen storage is a feature of late fetal life. Bile formation commences in the fourth month, however many enzyme methods are comparatively undeveloped till after start. The pancreas varieties from two buds and the acinar and islet cells develop facet by facet. The placenta due to this fact features for the fetus as its lungs, alimentary tract, liver and kidneys. To accomplish this effectively, it should convey the circulations of the fetus and mom into intimate contact but in a way that minimises exposure of the fetus to undesirable chemicals, microorganisms or immunological assault. The massive maternal vascular channels supplying the placenta are derived from trophoblastic invasion of the spiral arterioles within the endometrium. Where this process is defective, maternal blood supply of the placenta is reduced and preeclampsia and/or fetal progress restriction might result. The primitive trophoblast has opened up sinusoids crammed with menstrual blood in the endometrium. Chapter 2 Anatomy and Physiology of Pregnancy also encourages uterine leisure, thereby lowering the probability that the rapidly increasing conceptus shall be expelled by uterine muscular exercise. Formation of villi and the intervillous area From 12 days after conception, the trophoblastic cells send finger-like processes (villi) into the endometrium. In the mesenchymal core of the villi, fetal blood vessels develop and link via the physique stalk with the fetal vascular system. By day 18, the villi have branched several instances and both fetal and maternal blood vessels are functioning. The heart of the embryo begins to beat from approximately day 22 after fertilisation, making a practical circulation. The amnion lines the chorion laeve and fetal surface of the placenta, and turns into steady with the epithelial masking of the umbilical twine. The chorion laeve subsequently loses its villi and becomes the outer layer of the membranes, expanded into the cavity of the uterus by the amniotic membrane which becomes the inside amniotic layer. The increase in dimension of the placenta is comparatively less than that of the fetus so the fetal:placental weight ratio steadily will increase via pregnancy, reaching a value of 6:1 at term. That is, a fetus of delivery weight 3600 g at time period would have (on average) a placenta of weight of roughly 600 g. From the basal area, maternal blood enters 22 the cotyledon through the spiral arterioles. The blood enters within the type of spurts or jets and cascades down over the villi, that are floating within the intervillous area like seaweed within the ocean. Oxygen and nutrients are provided in change for carbon dioxide and waste products from the villi. The deoxygenated blood is carried away by giant veins, additionally situated on the basal area. The cotyledon is the unit of the placenta, and is predicated on the arteriolar vessels supplying it. The intervillous space is thus doubtlessly traversable throughout the whole placenta. These are anatomical rather than practical divisions, every containing numerous the latter.
Decadron 0.5 mg buy visa
There are eleven exterior intercostal muscle tissue acne pictures 1 mg decadron amex, which sit in the intercostal areas the areas between the ribs skin care 101 cheap decadron 1 mg without a prescription. Simultaneously the exterior intercostal muscles pull the rib cage outwards and upwards. The thorax is now greater than before and intrapulmonary stress is lowered under atmospheric stress in consequence. The most important muscle of inspiration is the diaphragm, 75% of the air that enters the lungs is because of diaphragmatic contraction. Airway resistance the flow of air by way of the airway passage depends on the resistance and strain distinction. The partitions of the airways supply some resistance to the circulate of air into and out of the lungs. During inspirations the bronchioles dilate as a result of their partitions are pulled in all instructions. Stimulation from the sympathetic nerve fibres causes the smooth muscular tissues to chill out leading to bronchodilation and decreased resistance. The greater the compliance the less effort is needed in chest and lung enlargement, and low compliance implies that extra effort is needed. In the lungs there are two components that play a component in compliance: the floor tension and elasticity. Normal lungs have a high compliance and expand easily as a end result of the elastic fibres stretch readily and surfactant in the lungs reduces surface rigidity. Lung volumes A wholesome adult at relaxation usually has a respiration fee of 1218 breaths per minute and with every respiration 500 ml of air is moved in or out of the lungs. This area is in the pons and is essential for regulating the quantity of air one takes in with every breath. When we discover ourselves needing to breathe quicker, the pneumotaxic space tells the dorsal respiratory group to velocity it up. And when we have to take longer breaths, the pneumotaxic area tells the dorsal respiratory group to delay its bursts. All the knowledge from the physique that should feed into the management of our breathing converges within the pneumotaxic space, so that it could properly regulate our breathing. Central chemoreception stays, on this means, distinct from peripheral chemoreceptors. This space sends alerts to the inspiratory space that activate and delay inhalation, leading to long, deep inhalation. When the pneumotaxic space is energetic, it overrides the signals from the apneustic space. Medullary rhythmicity space the function of this area is to control the respiratory rhythm. During quiet respiration, the inhalation is about 2 seconds whereas the expiration is 3 seconds. However, during forceful breathing the expiratory area is stimulated by nerves from inspiratory space. Stimulation by the expiratory area causes the intercostal and abdominal to contract, which causes a decrease within the thoracic cavity and forceful exhalation. This swelling is the carotid sinus, and it incorporates areas called carotid our bodies within it. These regions comprise our peripheral chemoreceptors, which detect oxygen levels directly. Each carotid physique is a couple of millimetres in dimension and has the excellence of having the best blood move per tissue weight of any organ within the physique. Afferent nerve fibres join with the sinus nerve earlier than getting into the glossopharyngeal nerve. A decrease in carotid physique blood circulate leads to mobile hypoxia, hypercapnia and decreased pH that result in an increase in receptor stimulation. The extra these neurons are energetic, the more they ship indicators into the pneumotaxic space and tell it to end this spherical of inspiration. These areas are discovered in the mind stem, and include neurons within them, central chemoreceptors, that detect adjustments within the carbon dioxide levels. When the carbon dioxide levels rise, that means that the respiration rate has to increase, eliminating the carbon dioxide and taking in additional oxygen. Instead, it changes into a bicarbonate ion, producing hydrogen ions as a by-product of this conversion. Central chemoreceptors Other influences on respiration Limbic system Temperature Can improve fee and depth of air flow in occasions of stress through inspiratory area stimulation. An increase or decrease in physique temperature can improve or lower the respiration rate, for instance fever and hypothermia, respectively. Pain A sudden extreme ache could cause a quick period of apnoea whereas a protracted somatic ache will increase the respiration rate. Irritation of airways Cessation of respiration can result from physical or chemical irritation of the pharynx. External respiration converts the oxygenated blood in the lungs to oxygenated blood earlier than the blood returns to the left facet of the heart. For this purpose the end portion of the bronchial tree is called the respiratory zone. The the rest of the bronchial tree from the trachea all the method down to the terminal bronchioles is the conducting zone. Diffusion occurs as a end result of fuel molecules all the time transfer from areas of high focus to low focus. Because cells are frequently utilizing oxygen, its focus inside tissues is all the time decrease than inside blood. Likewise the continual use of oxygen ensures that the extent of carbon dioxide inside a tissue is all the time larger than inside blood. As blood flows via the capillaries, oxygen and carbon dioxide comply with their pressure gradients and continually diffuse between blood and tissue. The concentration of oxygen in blood flowing away from the tissues, back towards the center is described as being deoxygenated. In reality if measured, the oxygen saturation of venous blood would probably be around 75%. This signifies that solely around 25% of oxygen content material (caO2) leaves the bloodstream, leaving a plentiful provide. Before oxygen can enter the internal environment and earlier than carbon dioxide can leave the internal environment they must cross the capillary and alveolar membranes. Simultaneously, carbon dioxide molecules depart the blood by diffusing down the carbon dioxide stress gradient out into the alveolar sac.
Cheap decadron 0.5 mg mastercard
Thus acne under chin decadron 8 mg discount without prescription, the reflex response to a fall in arterial pressure could acne rash generic 0.5 mg decadron mastercard, for instance, include a big improve in renal vascular resistance and a decrease in renal blood flow with out changing the cerebral vascular resistance or blood flow. The peripheral vascular changes associated with the arterial barorecep tor reflex happen primarily in organs with strong sympathetic vascular management. Other Cardiovascular Reflexes and Responses Seemingly in spite of the arterial baroreceptor reflex mechanism, giant and fast changes in mean arterial strain do occur in certain physiological and pathological conditions. These reactions are attributable to influences on the medullary cardiovascular centers apart from these from the arterial barorecep tors. The analogy was made earlier that the arterial baroreceptor reflex operates to control arterial strain somewhat as a house heating system acts to regulate inside temperature. Such a system automatically acts to counteract changes in tempera ture brought on by such things as an open window or a grimy furnace. One common operate that the cardiopulmonary receptors carry out is sensing the pressure or volume) in the atria and the central venous pool. Increased central venous stress and quantity trigger receptor activation by stretch, which elicits a reflex lower in sympathetic exercise. Chemoreceptors most likely play little function within the regular regulation of arterial pres positive because arterial blood Po2 and Pco2 are normally held very practically fixed by respiratory management mechanisms. An extremely strong response known as the cerebral ischemic response is triggered by insufficient brain blood circulate (ischemia) and might produce a more intense sym pathetic vasoconstriction and cardiac stimulation than is elicited by another affect on the cardiovascular management centers. However, if cere bral blood circulate is severely inadequate for several minutes, the cerebral ischemic response wanes and is replaced by marked lack of sympathetic activity. Presumably this case outcomes when perform of the nerve cells in the cardiovascular centers becomes directly depressed by the unfavorable chemical conditions within the cere brospinal fluid. Whenever intracranial stress is increased-for example, by tumor growth or trauma-induced bleeding inside the rigid cranium-there is a parallel rise in arte rial stress. This known as the Cushing reflex and is a variant of the cerebral isch emic response. It could cause imply arterial pressures of more than 200 mm Hg in severe cases of intracranial stress elevation. The obvious advantage of the Cushing reflex is that it prevents collapse of cranial vessels and thus preserves sufficient mind blood move within the face of huge will increase in intracranial pressure. The early phase of the Cushing reflex typically includes tachycardia, whereas the late (and more dangerous) phase of this reflex is accompanied by bradycardia (presumably resulting from elevated reflex vagal activity from the arterial baroreceptor input). These pathways may be activated 2 Certain different reflexes originating from receptors within the cardiopulmonary region have been described which could be essential in particular pathological situations. For instance, the Bezold-]arisch reflex that entails marked bradycardia and hypotension is elicited by software of strong stimuli to coronary vessel (or myocardial) chemoreceptors concentrated primarily within the posterior wall of the left ventricle. Activation of this reflex causes sure myocardial infarction sufferers to current with bradycardia as an alternative of the anticipated tachycardia. This enter could contribute to the marked improve in blood stress that accompanies such isometric efforts. It is uncer tain as to what extent this reflex contributes to the cardiovascular responses to dynamic (rhythmic) muscle train. The response serves to permit extended submersion by limiting the rate of oxygen use and by directing blood move to essential organs. A similar however much less dramatic dive reflex may be elicited in people by merely immersing the face in water. This is a uncommon exception to the general rule that sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves are activated in recipro cal trend. The dive reflex is sometimes used clinically to reflexly activate cardiac parasympathetic nerves for the aim of interrupting atrial tachyarrhythmias. Another, however unrelated, scientific approach for activating parasympathetic nerves in an try to interrupt atrial tachyarrhythmias is known as carotid mas sage. In essence, therapeutic massage of the neck is finished to trigger bodily deformation of the carotid sinuses and "trick" them into sending a "high-pressure" alarm to the medullary management centers. These responses originate within the cerebral cortex and reach the medullary cardio vascular centers by way of corticohypothalamic pathways. Excitement or a way of danger often elicits a fancy behavioral sample known as the alerting response (also known as the "defense" or "battle or flight" response). The cardiovascular element of the alert ing reaction is a rise in blood stress attributable to a common increase in cardio vascular sympathetic nervous activity and a lower in cardiac parasympathetic activity. Centers in the posterior hypothalamus are presumed to be concerned in the alerting reaction as a end result of lots of the parts of this multifaceted response can be experimentally reproduced by electrical stimulation of this area. The gen eral cardiovascular effects are mediated by way of hypothalamic communications with the medullary cardiovascular centers. The influences on the medullary cardiovascular facilities that produce vasovagal syncope seem to come back from the cortex through depressor centers within the anterior hypothalamus. It has been advised that vasovagal syn cope is analogous to the "taking part in lifeless" response to peril used by some animals. Fortunately, unconsciousness (combined with changing into horizontal) seems to quickly take away this critical disturbance to the normal mechanisms of arterial stress control in humans. The extent to which cardiovascular variables, particularly blood stress, are normally affected by an emotional state is currently a topic of utmost curiosity and appreciable research. The concept is that the same cortical drives that provoke somatomotor (skeletal muscle) exercise also simultane ously initiate cardiovascular (and respiratory) changes applicable to help that activity. In the absence of another obvious causes, central command is at current the best clarification as to why each mean arterial pressure and respiration improve throughout voluntary exercise. Generally, superficial or cutaneous pain causes an increase in blood pressure in a person ner just like that associated with the alerting response and perhaps over lots of the identical pathways. This response could contribute to the state of shock that often accompanies crushing injuries and/or joint displacement. Dilation of cutaneous vessels promotes heat loss (as lengthy as the environmental temperature is under the body temperature). Temperature regulation responses are controlled primarily by the hypothalamus, which can operate via the cardiovascular facilities to discretely control the sympathetic exercise to control vasoconstric tion of cutaneous vessels and thus skin blood flow. Measurable adjustments in cutaneous blood circulate result from changes in hypo thalamic temperature of tenths of a level Celsius. Cutaneous vessels are influenced by reflexes concerned in each arterial pressure regulation and temperature regulation. This figure is meant first to reemphasize that the arterial baroreceptors usually and con tinually supply the main enter to the medullary facilities. The arterial baroreceptor input is proven as inhibitory as a result of an increase in arterial baroreceptor firing fee leads to a lower in sympathetic output. Central venous pressure (cardiopulmonary baroreflexes) Cutaneous pain Raise set point i Intracranial strain (Cushing reflex),J.
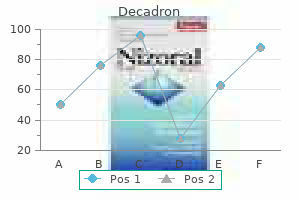
Decadron 1 mg without a prescription
Time of hematuria throughout micturition can differentiate websites of bleeding: Visible hematuria initially of micturition and subsequent clearing of urine-urethral bleeding-"Initial hematuria" skin care during winter buy generic decadron 0.5 mg line. Visible hematuria on the finish of micturition called "Terminal hematuria"-indicates skin care routine for oily skin discount decadron 4 mg without prescription, bleeding from bladder or prostate. Visible hematuria with episodes of pharyngeal infection-or exercise-IgA nephropathy. Acquired: Infection: � Urethritis � Cystitis � Acute pyelonephritis � Pyelitis � Prostatitis. Gastroenterology and Urinary System Traumatic: 577 Urethral stricture Stone Instrumentations Trauma Sudden decompression of bladder in case of acute retention of urine � Exercise � Radiation. Concomitant color of plasma: If colour of plasma is red-it suggests presence of hemoglobin in plasma, not myoglobin- because myoglobin is quickly cleared off from the blood. Myoglobinuria Excretion of myoglobin from broken muscles-released in urine-producing myoglobinuria. In kids and adolescent-normal urinary protein excretions twice the amount excreted by adult. In these instances, affected person usually complains of frothing of urine throughout micturition. This is due to improvement of fistula tract between alimentary tract and urinary tract. Urethral Discharge Purulent discharge per urethra-between the instances of micturition. History is like: Discharge of whitish pus like secretion per urethra Staining of underwear with yellowish secretion Any ache throughout micturition Whether the discharge accommodates blood. Purulent discharge: Thick yellowish green: Gonococcal urethritis Chronic prostatitis. Pain Due to Renal Cause Pain in loin-colicky in nature-radiating to groin, scrotum, or labia-acute urinary tract obstruction. Gastroenterology and Urinary System 579 In contrast-chronic urinary tract obstruction: the extent of bladder-hesitancy, poor move and terminal At dribbling. In case of perirenal abscess-pain in loin-radiates alongside the tract via which pus will cross or could affected person complains of cough, chest pain as a result of diaphragmatic irritation. Past medical history: Recent renal disease may be the penalties of either past medical disease or its complication or the complication of treatment. Childhood recurrent urinary tract infection, late nocturnal enuresis-may be because of vesica-ureteral reflux, which can be responsible for future persistent pyelonephritis. Systemic lupus erythromatosus-early involvement of joint and skin-later on involve progressive renal illness. Oncological drugs-cyclophosphamide-produce hematuria, afterward develop bladder cancer. Cirrhosis with ascites-may produce hepatorenal syndrome Infective diarrhoea might produce hemolytic uremic syndrome Tuberculosis could also be answerable for: Urogenital tuberculosis Amyloidosis Sterile pyuria. Gynecological historical past: Patient with chronic renal disease might produce menorrhagia because of improvement of platelet abnormalities and coagulation abnormalities. In case of pregnant patient-pregnancy induced hypertension may produce proteinuria, edema-may precipitate renal failure. Drug history: A small amount of any drug may be responsible for allergic nephritis. Few antihypertensive drugs-angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blockers-may be dangerous in affected person with renal artery stenosis, as a result of they could produce deterioration of renal perform. Oral contraceptive drugs, corticosteroids could also be answerable for hypertensive renal disease in case of long-term use. Dietary history: High protein, high K+ containing fruits (citrus fruit) could produce cardiovascular complication or deterioration of consciousness in patient with chronic kidney illness not in hemodialysis. High salt and water content material may produce circulatory overload and respiratory misery because of growth of pulmonary edema. High animal protein, calcium, purine containing greens could additionally be liable for gouty nephropathy. High consumption of fruit juice or acidic meals could increase K+ intake produces worsening of cardiovascular symptom or increase oxalate content material producing urate nephropathy. High intake of tea or espresso, which comprise methylxanthine answerable for polyuria. Gastroenterology and Urinary System 581 In high socio-economic status: High protein containing food plan Increase consumption of tobacco is related to growth of atherosclerosis, may worsen chronic kidney illness. Illicit drug use-may be responsible for: Glomerulonephritis Acute renal failure Vasculitis Rhabdomyolysis. Excessive publicity to very hot climate-increase the urinary concentration-responsible for renal stone formation. Exposure to infection: Leptospirosis-in sewage workers, farm workers Hantavirus-in laboratory staff handling rodents. Family history: this is answerable for identification of few family related diseases. Other inherited problems: von Hippel-Lindau illness Congenital nephritic syndrome. Tubular illness: Renal tubular acidosis Cystinuria Nephrogenic diabetes incipidus. Geographical influences: In black African Caribbean: affected person with diabetes hypertensive renal failure is extra In common. In Indian and Russian inhabitants, incidence of tuberculosis is more common in immunosuppressive affected person getting immunosuppressive remedy after transplantation. Perioral hyperpigmentation-Peutz-Jeghers syndrome-associated with hamartomatous polyps in jejunum. Oral and tongue telangiectasias-Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome -associated with gastrointestinal tract lesion with iron deficiency anemia. Symmetrical yellowish plaques round eyelids-xanthelasma - primary or secondary biliary cirrhosis. Wide set eyes, outstanding brow, flat nostril, small chin, persistent intrahepatic cholestasis in childhood. Jaundice-yellowish discolorations of conjunctive and skin- any trigger producing jaundice. Vitiligo-patchy cutaneous depigmentation-immune destruction of melanocytes-autoimmune hepatitis Primary biliary cirrhosis. It could be described as: Central arteriole with radiating capillaries from central arteriole present in. Livedo reticularis: Dark pigmented pores and skin, brown skin having hyperpigmented reticulated pattern.
Syndromes
- Esophageal stricture after surgery or endoscopic therapy
- Headache
- Manage high blood pressure.
- Leave words out of sentences when talking
- Headache
- High blood ammonia level
- Activated charcoal
1 mg decadron purchase with amex
Patients already established on a -blocker ought to continue due to the chance of rebound tachycardia rising myocardial oxygen demand with elevated threat of myocardial ischaemia acne vulgaris pictures order 8 mg decadron visa. Due to the numerous danger of intra- and postoperative hypotension, the anaesthetist may decide whether or not to omit these medication perioperatively acne 5 skin jeans decadron 4 mg buy generic online. They are significantly susceptible to postoperative issues such as respiratory failure and pneumonia, requiring respiratory support including ventilation. The perioperative management of sufferers with respiratory disease is mentioned within the following sections. Diabetic comorbidity Vascular disease Diabetics develop each a specific microangiopathy (typified by diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy) and macrovascular illness with accelerated atherosclerosis that leads to elevated threat of ischaemic coronary heart illness, cerebrovascular accident, peripheral vascular illness, renovascular illness, hypertension and delayed wound therapeutic. Due to an absence of renal reserve, diabetics are particularly susceptible to acute renal failure ensuing from hypotension, nephrotoxic drugs, radiological distinction agents and sepsis. A important proportion of patients growing postoperative renal failure will remain dialysis dependent. It is subsequently crucial that care is taken to guard towards further kidney insult. Anaesthetic technique General anaesthesia is associated with a threat of respiratory problems, in part due to altered respiratory perform caused by general anaesthesia. This is of explicit concern in patients with preexisting respiratory disease and decreased respiratory reserve. Regional anaesthetic methods may reduce or eliminate the necessity for basic anaesthesia in this group. Neuropathy Diabetic neuropathy is most commonly encountered by the vascular surgeon in association with limb ischaemia as a component of nonhealing ulceration. Autonomic neuropathy should be anticipated and can end result in delayed gastric emptying with risk of aspiration during induction of anaesthesia. A lack of sympathetic cardiovascular compensation to anaesthetic-induced hypotension or bleeding can lead to extreme hypotension. Regional anaesthetic strategies, notably epidural analgesia or other regional methods, are efficient in this regard. Parenteral opiates are efficient analgesics but care should be taken to not cause respiratory despair or obtund the aware level. Infection Diabetic sufferers are at elevated danger of infective complications, particularly if glycaemic control is poor. Effect of surgical stress on diabetic management Part of the metabolic response to surgical procedure entails glucose mobilisation and lipolysis with elevated circulating insulin ranges to maintain up homeostasis and normoglycaemia. The internet lead to diabetics is a tendency in path of hyperglycaemia and ketoacidosis following surgery, which is exaggerated if complications similar to sepsis develop. Glycaemic control should be monitored carefully and insulin or oral hypoglycaemic drug doses titrated accordingly. Physiotherapy Pre- and postoperative chest physiotherapy is essential in sufferers with respiratory disease. Manoeuvres that facilitate maximal inspiratory effort, optimistic airway pressure and using incentive spirometry are notably helpful in minimising the chance of atelectasis and guarding against hypoxia and pneumonia. Principles of perioperative diabetes administration the purpose of perioperative diabetic administration is to hold up steady circulating glucose levels, ensuring an enough gas provide to the cells. As hypoglycaemia is more dangerous to the affected person than hyperglycaemia, moderate hyperglycaemia is appropriate. Care ought to be taken to manage sufficient potassium when insulin is administered as insulin increases mobile potassium uptake, with an inclination in direction of hypokalaemia. In follow, many units have protocols for the perioperative administration of diabetes, which may be tailored to the person affected person. Postoperative ventilation Postoperative ventilation may be indicated for respiratory failure as a result of insufficient respiratory reserve or problems similar to pneumonia. Meticulous consideration to analgesia and regular chest physiotherapy might avoid the necessity for air flow. The length of endotracheal intubation must be minimised as a result of it also will increase the danger of pneumonia. Diabetes mellitus the increased perioperative danger related to diabetes mellitus is attributable to related comorbidities and poor glycaemic control, which is exacerbated by surgical stress. Sliding scale insulin regimens include intravenous insulin, glucose and potassium that can be given as a single combined infusion (the Alberti regimen) (Table 5. Single mixed infusions are easy, low-cost and safer, with less threat of hypoglycaemia, however on the expense of greater flexibility and tight glycaemic control that might be achieved with separate insulin and glucose infusions. Dialysis-dependent patients Considerations in dialysis-dependent sufferers include: � Fluid steadiness. The majority of these sufferers are anuric and depend upon dialysis to remove excess water. Management of fluid steadiness and specific arrangements for dialysis must be undertaken at the aspect of a nephrologist. Patients will either have venous access for haemodialysis (fistulae or large intravenous cannulae) or peritoneal dialysis catheters. An arteriovenous or dialysis entry graft ought to never be used for intravenous access or phlebotomy. Clotting should be corrected preoperatively by administration of intravenous vitamin K or fresh-frozen plasma if pressing. Acute renal failure Acute renal failure generally accompanies jaundice and is referred to as hepatorenal syndrome. An imbalance in vascular tone exists, with disturbances in systemic haemodynamics, elevated vasoconstriction, and a reduction within the activity of the vasodilator methods. Patients with hepatorenal syndrome sometimes have an increased cardiac output, low blood pressure, reduced systemic vascular resistance, and elevated renal vasoconstriction. They are at risk in the course of the perioperative interval of deteriorating renal operate that renders them dialysis dependent. The threat of further deterioration in renal perform could be lowered by: � Optimising fluid balance directed by central venous pressure monitoring � Avoiding nephrotoxic medication. Cirrhosis Cirrhotics have considerably increased perioperative morbidity and mortality, which is related to the degree of hepatic decompensation and kind of surgical procedure. Nonalcoholic fatty liver illness is more and more recognised as a part of the metabolic syndrome. It is associated with weight problems and has been demonstrated to convey an extra threat for postoperative morbidity and mortality in sufferers present process major liver resection. A number of algorithms have been used to estimate postoperative mortality on this patient group, including the modified Childs score (see Chapter 14). This stratifies prothrombin time, albumin, the presence of ascites, encephalopathy and bilirubin to generate a rating. Scores of A, B and C are related to perioperative mortalities of 10, 30 and 80%, respectively, for belly surgery.
Buy decadron 4 mg mastercard
Ventral respiratory group within the nucleus ambiguous and nucleus retroambiguous-responsible for active respiration at increased breathing rates acne kids decadron 4 mg buy visa. After abolishment of all afferent impulses acne 6 months after giving birth 1 mg decadron purchase free shipping, the above inspiratory cells ship repetitive burst of lively potentials, which is responsible for contraction of respiratory muscles. Peripheral chemoreceptor: � Carotid bodies on the bifurcation of the widespread carotid arteries. Type one cells include dopamine and are close apposition to endings of the afferent carotid sinus nerves. Lung receptors: Pulmonary stretch receptor (slow adapting receptor): � Present in airway smooth muscle � They are activated in response to distension of lung � the impulse travels through vagus nerve (large myelinated fibers) � Main response is slowing of respiratory frequency-due to increase in expiratory time-known as Hering-Breuer inflation � Recent work suggests that these reflexes are largely inactive in adult human unless tidal quantity exceeds 1 liter, as in train. Irritant receptor (rapidly adopting pulmonary stretch receptor): � these lie in between airway epithelial cells � Stimulated by noxious gases, cigarette smokes, inhaled dust, and cold air � Impulses travel by myelinated vagal nerve fibers � Effector response is bronchoconstriction. Bronchial C fibers: � these are current within the bronchial wall close to bronchial circulation � Stimulated by chemical substances in bronchial circulation � Effector response is speedy shallow respiratory, bronchoconstriction and mucus secretion. Joint and muscle receptor: � Impulses from moving limb � Stimulates ventilation throughout exercise. Gamma system: � Muscle spindles within the intercostals and diaphragm stimulated in response to elongation of muscle fibers � It controls power of contraction, could produce dyspnea. Arterial baroreceptor: � Increase within the arterial blood stress, could cause reflex hypoventilation and apnea, when aortic carotid sinus baroceptors are being stimulated � Decrease of blood stress produces hyperventilation. Pain, temperature receptors: � Pain receptor stimulation produces period of apnea adopted by hyperventilation � Heating or warming the skin produce hyperventilation. Physiology of Pleural Fluid Absorption and Reabsorption Amount of fluid in regular human being pleural cavity is 1 to 20 mL. In case of parietal pleura: z Capillaries around the parietal pleura = 30 cm of water z Pleural strain = � 5 cm of water in between the pleural layer z So net pressures = 30 � (�5) = 30 + 5 = 35 cm of water. It is answerable for driving the fluid into the pleural cavity z Colloid stress in capillaries = 34 cm of water z Colloid osmotic pressure of the pleura = eight cm of water z So net strain = (34�8) cm of water = 26 cm of water, which is responsible for driving the fluid from the pleural area into pulmonary capillaries z So, balance drive is 35 � 26 = 9 cm of water, which directs the fluid from the parietal pleura into pleural cavity. Normal Values Respiratory stress is at all times expressed in relation to atmospheric stress (760 mm Hg). Elastic arteries: these include: Main pulmonary artery and its following branches extending approximately to the junction of bronchi and bronchioles: Lobar branches Segmental branches Subsegmental branches. Muscular arteries: They have exterior diameter of 70 to 500 mm and have nicely developed layer of circular clean muscle cells between elastic lamina. Below 70 mm diameter, these vessels progressively free smooth muscular tissues, turns into arterioles, having intima and elastic lamina. Arterioles: Within the acinus, it divides along with accompanying branches of acini and give some accent branches. These branches are terminated round alveolar sac; break up into capillaries around alveoli. Other Accessory Vessels these are supplementary branches of pulmonary artery immediately penetrate into lung parenchyma. These branches arise from the whole size of arterial tree and increase towards periphery. So the branching ratio (average variety of daughter branches originating from one father or mother branch) will increase as the vessel measurement decreases. Respiratory System 169 Pulmonary Veins Pulmonary vein arises from capillaries of the arteriolar network. Two massive inferior pulmonary veins drain the blood from: lower lobes of each the lungs. Bronchial Arteries Two to four bronchial arteries directly come up from: z Aorta z Intercostals vessels. Near the hila, these branches to form intercommunicating community of circular arc around the primary bronchi from these arterial community, intrapulmonary arteries radiate-these branches current within peribronchial connective tissue and divide along the branches of airways up to terminal bronchioles. Anterior parietal (internal mammary lymph nodes): � Situation: Upper portion of thorax behind anterior intercostal areas bilaterally � Drainage area: Anterior chest wall, medial portion of breast, sure portion of diaphragm, upper anterior abdominal wall. Posterior parietal lymph nodes: � Present adjacent to rib heads in posterior intercostal areas (intercostal nodes) or adjoining to vertebrae (juxtavertebral) � Drainage space: Intercostal spaces, parietal pleura, vertebral column. Anterosuperior mediastinal nodes: these groups drain the structures of anterior pericardium, thymus, diaphragmatic and mediastinal part of the guts and anterior portion of hila. Posterior mediastinal (periesophageal) lymph nodes and periaortic nodes: Drainage areas: Posterior portion of diaphragm, pericardium, esophagus and lower lobes of lungs. Tracheobronchial lymph nodes: these are subdivided into following subgroups: Paratracheal: Afferent from bronchopulmonary nodes, tracheal bifurcation nodes, trachea, esophagus, proper and left lung directly Tracheal bifurcation (carinal) nodes: Situated in precranial, and subcranial fats and across the circumference of right and left major bronchi Aortopulmonary window nodes: Divided into medial, lateral and superior groups. Afferent from bronchopulmonary nodes, mediastenal nodes, heart, pericardium, esophagus and lungs Hilar nodes: Located around the principle bronchi. Size of the nodes: z Upper paratracheal and left paraesophageal nodes ought to be declared enlarged when the diameter is >7 mm z Anterior mediastinal nodes are >8 mm z Lower paratracheal and proper paratracheal nodes are >10 mm z Subcarinal nodes are >11 mm. Cough It is an explosive expiration to protect the lung from aspiration and to advertise secretion and other constituent upwards towards the mouth. Cough is a sort of protecting in addition to cleansing mechanism: z Cause: It arises from irritation of cough receptors within the trachea, pharynx, larynx, and bronchi by: Infection Inflammatory exudates in the airways or parenchyma Tumor Foreign body, inhaled particles Parietal pleura-on uncommon occasion during aspiration of pleural effusion Cerumen in the external ear Pressure on the external wall of bronchus. Involuntary mechanism often entails: z Mechanical and chemical: Inhalation of irritants like, smoke, mud, distortions of airways by pulmonary fibrosis or atelectasis. Causes and Characteristics of Cough Causes Pharynx Larynx Characteristics Pharyngitis-upper respiratory tract sneezing, nasal allergy, sore throat symptoms like, Epiglottal disease Barking cough Laryngitis, whooping cough, croup, Laryngeal tumor. Harsh, barking, painful, persistent, associated with stridor Left-sided vocal cord paralysis-Bovine cough, inefficient, low pitched accompanied by hoarseness of voice Tracheitis producing dry painful cough, sore throat, operating nostril (stridor) Bronchitis-dry or productive on most of the days for >3 consecutive months and for >2 years, worse in morning, sputum is mucoid Asthma-dry with scanty and sticky sputum, worse at night time Bronchogenic carcinoma-cough with productive or nonproductive for month or years, with occasional hemoptysis Brochiectasis-long-standing cough with large amount of mucoid or foul smelling purulent sputum, amount adjustments with posture Lobar pneumonia-proceeded by higher respiratory tract signs, cough painful and dry at first, followed by productive later Bronchopneumonia-cough is dry or productive Exacerbation of chronic bronchitis-cough, first dry then mucoid adopted by purulent Contd. It is usually accompanied by heart burn, belching Associated with eating and drinking-neuromuscular disease of upper esophagus Foreign body When in higher airway-cough associated with stridor and asphyxia. Later in lower airways-nonproductive and localized wheeze Left ventricular failure-cough aggravated in supine position, decreased in recumbent position Pulmonary infarction-cough associated hemoptysis may be pleural effusion Drug with Cardiovascular Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor-nonproductive cough, often in girls, could begin with graduation of drug on years after use Morning: Smoking Nocturnal: Postnasal drip, congestive cardiac failure Debility and weak spot Inadequate coughing Time of cough Type of Cough Dry hacking cough Chronic productive Barking Morning cough Nocturnal cough Stridor Associated with consuming or ingesting Inadequate coughing Wheezing Allergy, viral an infection, anxiety neurosis, tumor, interstitial lung disease Bronchiectasis, lung abscess, chronic bronchitis, bacterial pneumonia, tuberculosis Epiglottic illness Smoking Congestive cardiac failure Tracheal obstruction Upper esophageal muscular disease Debility, weak spot Asthma, allergy, persistent obstructive lung illness 174 Clinical Methods and Interpretation in Medicine Mechanism of Cough Rapid inspiration followed by following processes in fast sequences: z Closure of glottis z Contraction of thoracic and stomach expiratory muscles z Abrupt improve of intrathoracic stress (100�200 mm Hg) z Sudden opening of glottis z Explosion of burst of air through mouth. Production of sound during cough by: z Vibration of intra-airway secretions z Vibrations of tracheobronchial partitions z Vibration of parenchyma. Neural Pathways within the Development of Cough Afferent pathways z fifth nerve carrying impulses from nose and sinuses z ninth nerve carrying impulses from posterior pharynx z 10th nerve carrying impulses from larynx, trachea, bronchi, pleura, and pericardium z Phrenic nerve carrying impulses from trachea, bronchi, esophagus, abdomen, and pleura. Most of the receptors are concentrated in the larynx with gradual lower in focus of receptors down the tracheobronchial tree. Efferent pathways z 10th nerve carrying impulses to larynx, trachea, and bronchi z Phrenic nerve carrying impulses to diaphragm z Spinal motor nerve to expiratory muscles of the rib cage. Damage of reflex pathways z Bronchiectasis harm the irritant receptors on the bronchial wall z Narcotics and anesthetics lower the sensitivity of the receptors z Tracheostomy eliminates the glottis closure z Neuromuscular disease weakens the respiratory muscular tissues z Age weakens the respiratory muscles. Regarding sputum one has to ask the patient: z Show me what you want to do to get phlegm up z If patient denies sputum-a cough producing rattle (loose cough)-suggests its presence. Following informations should be asked relating to sputum: z Amount: may be very large (a teacupful per day) It Causes: � Bronchiectasis � Lung abscess � Bronchoalveolar cell carcinoma. Very small amount (one to 2 spits per day) � Early phase of pneumonia � Bronchial bronchial asthma. Yellow, green, brown sputum: Lung infections-all types- bronchopulmonary infection in bronchiectasis and continual bronchitis Rusty sputum: Pneumococcal pneumonia Pink frothy sputum, frothy sputum with streak of blood: Pulmonary edema Black coloured sputum: Town dweller Red present jelly: Klebsiella pneumoniae infection Pink blood tinged sputum: Streptococcal or staphylococcal pneumonia Bloody sputum: Pulmonary emboli, tuberculosis, bronchiectasis, bleeding disorders. Small bronchial forged like twigs: Bronchopulmonary aspergillosis associated with asthma. Taste or odor: Foul smelling sputum: Lung abscess Infected bronchiectasis Infection with anaerobic organism.
1 mg decadron buy with visa
A polypeptide natri uretic (salt-losing) issue has been identified in granules of cardiac atrial cells skin care yang bagus untuk jerawat purchase decadron 1 mg line. Atrial distention causes the release of this atrial natriuretic peptide into the blood skin care doctors edina decadron 4 mg buy without a prescription. The chance that the center itself may function an endocrine organ within the regulation of physique fluid quantity is stimulating a lot analysis interest. This is a really speedy and highly effective mechanism that basically keeps inner osmo larity constant in the lengthy term. The bottom line for us is that, given fixed internal osmolarity, whole extracellular volume should at all times parallel any modifications in whole extracellular solute content material. That is the primary cause that renal sodium dealing with is of paramount importance in regulating extracellular quantity. Most essential, this figure exhibits that urinary output price is linked to arterial pressure by many synergistic pathways. Because of this, modest changes in arterial stress are related to massive adjustments in urinary output price. Glomerular capillary strain t Renal arteriolar vasoconstriction t Renin launch J. At the core of this hypothesis is the indisputable fact that in the long term (months, years, lifetimes) our urinary fluid output must exactly match our extremely variable fluid input. Any hypothesis about long-term management of arterial pressure (or another life variable for that matter) must ultimately work within this con straint. Moreover, the 2 known (but admittedly very rare) particular causes of hypertension (renal artery obstruction or excess aldosterone production from an adrenal gland adenoma) each point to the kidneys. One widespread hypothesis along these strains is that: "Long-term arterial pressure is regulated to be whatever it must be to maintain enough mind blood circulate. It is essentially unknown to what extent these "other" influences may be involved in long-term pressure regulation. The bottom line of all that is that the interaction of all the components concerned within the long-term management of arterial pressure continues to be an lively matter of debate. We remind the coed that, regardless of the purpose of long-term arterial pres positive regulation, changes in imply arterial stress may be accomplished solely by altering cardiac output and/or complete peripheral resistance. Hopefully, this debate will ultimately end in some melding of the theories that can improve our understanding of what fac tors trigger chronic hypertension. The arterial baroreceptor reflex is liable for regulating arterial stress in the brief term on a second-to-second and moment-to-moment basis. The arterial baroreceptor reflex entails the next: strain sensing by stretch delicate baroreceptor nerve endings in the walls of arteries; neural integrating facilities in the brainstem that adjust autonomic nerve exercise in response to the pressure info they receive from the arterial baroreceptors; and responses of the guts and vessels to adjustments in autonomic nerve activity. Overall, the arterial baroreflex operates such that an increase in arterial pressure leads to an primarily instant lower in sympathetic nerve exercise and a simultaneous enhance in parasympathetic nerve exercise (and vice versa). Massage of the neck over the carotid sinus space in a person experiencing a bout of paroxysmal atrial tachycardia is often effective in terminating the episode. Indicate whether imply arterial stress, in any case reflex adjustments are made, will be increased or decreased by the following stimuli: a. Describe the quick direct and reflex cardiovascular consequences of giving a wholesome particular person a drug that blocks a,-adrenergic receptors. Describe the potential changes in imply arterial pressure, sympathetic nerve activity, cardiac output, complete peripheral resistance, and shifts in the cardiac operate and venous return curves. What internet short-term alterations in mean arterial stress and sympathetic activ ity would the next produce Your patient has lower-than-normal imply arterial strain and higher-than normal pulse price. In basic, regular kidneys are inclined to retain sodium and fluid within the body each time a. Lists how the primary disturbances change the affect on the medullary cardio vascular facilities from (1) arterial baroreceptors and (2) other sources. States what instant reflex compensatory changes will happen in sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve actions on account of the altered influences on the medullary cardiovascular facilities. Indicates what quick reflex compensatory adjustments will occur in primary cardiovascular variables similar to the center fee, cardiac contractility, stroke volume, arteriolar tone, venous tone, peripheral venous strain, central venous strain, complete peripheral resistance, resistance in any major organ, and blood flow by way of any main organ. Predicts what the online impact of the first disturbance and reflex compensatory influences on the cardiovascular variables listed within the previous objective will be on mean arterial stress. States whether imply arterial pressure and sympathetic nerve activity will settle above or beneath their regular values. Predicts whether or not and states how cutaneous blood flow will be altered by tempera ture regulation reflexes. Indicates whether and how transcapillary fluid movements might be involved in the total cardiovascular response to a given main disturbance. Indicates whether, why, how, and with what time course renal adjustments of fluid balance will take part within the response. Predicts how each of the essential cardiovascular variables might be influenced by longterm adjustments in blood quantity. The scholar understands how respiratory activities affect the cardiovascular system: Describes how the urespiratory pumpu promotes venous return. Identifies the first disturbances on cardiovascular variables related to regular respiratory activity. The pupil understands the precise processes associated with the homeostatic adjustments to the consequences of gravity: States how gravity influences arterial, venous, and capillary pressures at any height above or beneath the guts in a standing particular person. Describes and explains the adjustments in central venous strain and the changes in transcapillary fluid stability and venous quantity within the lower extremities attributable to standing upright. Describes the operation of the nskeletal muscle pumpn and explains the way it simulta neously promotes venous return and reduces capillary hydrostatic strain in the muscle vascular beds. Identifies the primary disturbances and compensatory responses evoked by acute modifications in body place. The pupil understands the particular processes associated with the homeostatic changes to exercise: Identifies the primary disturbances and compensatory responses evoked by acute episodes of dynamic train. Describes the conflict between strain reflexes and temperature reflexes on cuta neous blood move. Indicates how the uskeletal muscle pumpu and the urespiratory pumpu contribute to cardiovascular adjustments during train. Compares the cardiovascular responses to static train with those to dynamic train. Lists the consequences of chronic train and physical conditioning on cardiovascular variables. The student understands the cardiovascular alterations that accompany pregnancy, start, progress, and growing older: Identifies the major maternal cardiovascular adjustments that occur throughout being pregnant. Follows the pathway of blood move through the fetal coronary heart and describes the changes that occur at start. Indicates the normal modifications that occur in cardiovascular variables throughout childhood. Identifies age-dependent changes that happen in cardiovascular variables similar to cardiac index, arterial strain, and cardiac workload.
Decadron 0.5 mg discount overnight delivery
The palms and forearms are wetted under a working tap and totally washed with an antiseptic resolution similar to povidone-iodine (Betadine) or chlorhexidine (Hibiscrub) � A sterile brush is then used to scrub the palms: in particular, the ulnar border, the interdigital clefts and the nails � After the wash is accomplished, the palms are rinsed and held hands up/elbows down, so that water from the hands runs from the elbows into the sink � the palms are dried on a sterile towel and the operator puts on a sterile robe and gloves acne location meaning buy decadron 0.5 mg otc. Thereafter, the operator should not contact anything other than sterile equipment or devices � the operative area is now cleansed with an antiseptic answer such as povidone-iodine or chlorhexidine, using sterile instruments and swabs acne xylitol discount decadron 8 mg without a prescription. The area prepared ought to be much higher than the anticipated operative field, and cleaning should start from the centre and work outwards � the operative subject is then encircled with sterile drapes, which are secured in order to depart the operative area on the centre and supply the operator with as extensive a sterile surrounding as possible. Suture materials Nonabsorbable sutures Nonabsorbable sutures could also be categorised into three teams: 1. Their disadvantage is increased tissue reaction and suture line sepsis, brought on by the capillary action of the braided material drawing microorganisms into the suture track. They are free from the capillary impact of braided sutures and cause much less suture monitor sepsis. Knots in monofilament sutures are much less safe than these in braided or pure sutures, and most surgeons use a quantity of throws when knotting monofilament sutures. It is finest practice to calculate the utmost beneficial dose for any native anaesthetic and if a bigger volume is required (for instance to infiltrate a wide area) the maximum recommended quantity of native anaesthetic may be diluted with 0. Lidocaine (lignocaine), the most widely used native anaesthetic agent, is out there in 0. Lidocaine is a short-acting anaesthetic (lasting as much as 2 hours) whereas bupivacaine is a longer acting native anaesthetic that lasts up to 8 hours. It is permissible to mix native anaesthetics, although the maximum really helpful quantity might be correspondingly smaller. Solutions of local anaesthetic mixed with a 1:200,000 focus of adrenaline (epinephrine) can be found. It minimises bleeding and reduces redistribution of the anaesthetic agent, rising its efficacy and length of action. Absorbable sutures Absorbable sutures are generally produced from artificial materials. They cause relatively little tissue response, retain their tensile power and are absorbed slowly. These synthetic sutures are commonly used for intraabdominal procedures and subcuticular wound closure. Interrupted sutures with each knot buried are used for small wounds, whereas in longer wounds a continuous subcuticular suture is employed. Suturing the skin Skin wounds are sutured beneath as near-sterile conditions as possible, utilizing a strict aseptic approach. A few primary ideas underlie good wound care: � Tissue must be handled gently. Where this is prevented by heavy contamination, delayed major closure or secondary closure must be thought-about. Suturing the purpose of suturing is to approximate tissues to facilitate major wound therapeutic to happen, or to ligate bleeding vessels to arrest haemorrhage. Straight needles and enormous curved needles are usually hand-held, whereas smaller curved needles are designed to be used with a needle holder. Round-bodied needles push tissue aside somewhat than reduce through and are most popular when stitching blood vessels and bowel. This allows the tongue and soft tissues to fall clear of the larynx and supply a patent airway. The mouth and pharynx should be checked and cleared of particles, corresponding to dentures, vomit or food. The mouth is opened barely and the mandible pulled firmly forward by stress utilized behind each angles of the jaw. The mandible is held on this position by closing the mouth and utilizing the teeth as a splint. Forward pressure is maintained behind the angles of the jaw (jaw-thrust manoeuvre) or submentally (chin-lift manoeuvre), avoiding pressure on the soft tissues. In some instances, notably in edentulous patients, an oropharyngeal airway helps to maintain a patent airway. If sutures are knotted too tightly, the suture line might turn out to be ischaemic, leading to delayed therapeutic, nonhealing and an elevated danger of wound an infection, and in excessive situations sutures can cut through. Equally, insufficient tension on the suture could lead to failure to appose the wound edges or inadequate haemostasis. Interrupted sutures have the benefit over a continuous suture in that the removing of one or two appropriately sited stitches might allow enough drainage if the wound turns into contaminated. A enough quantity ought to be inserted to take care of apposition without the skin edges gaping. The size of chew is decided by the quantity of subcutaneous fats and by whether or not the fat has been separately sutured. For stomach wounds, 5-mm bites are taken on both side of the wound, whereas on the face a 1�2-mm bite is most popular. The wound edge is picked up with toothed dissecting forceps, then the needle is launched via the pores and skin at an angle as near vertical as attainable and introduced out on the opposite side at an analogous angle. A subcuticular continuous suture is preferred by some surgeons and avoids the small pinpoint scars at the web site of entry and exit of interrupted sutures, or the cross-hatching that results if sutures are tied too tightly or left in too long. Cosmetic results as good as those achieved by subcuticular suturing could be obtained by removing sutures in half the times listed in Table eight. Skin stapling is commonly used for closure of wounds at any site, as it can be undertaken quickly. The staples are provided in disposable cartridges for single patient use and are easily eliminated. Ventilation by mask the lungs may be ventilated by masks and bag, utilizing considered one of two techniques. The first is a rebreathing bag with an adjustable valve and contemporary gasoline provide (which should be present in each anaesthetic room, intensive therapy unit and resuscitation room). In the unconscious affected person, muscle tissue that normally keep a transparent airway become lax. The tongue and soft tissue fall backwards, notably within the supine affected person, occluding the airway. Maintaining a transparent airway allows the affected person to breathe or permits the lungs to be ventilated. For the inexperienced, this method is greatest performed with the help of an assistant. A mask is applied to the face and held in position utilizing the thumb and index fingers of both arms. The little fingers of each hand are positioned behind the angles of the jaw and used to raise the mandible forward. The ring and center fingers are placed on the mandible to assist maintain this position. Larynx Trachea 8 the laryngeal masks airway Oesophagus this airway gadget is designed to be inserted into the pharynx, and has a cuff that, when inflated, types a gentle seal over the larynx.
