
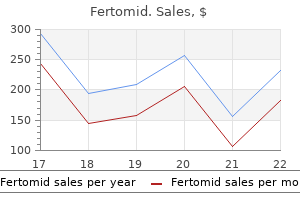
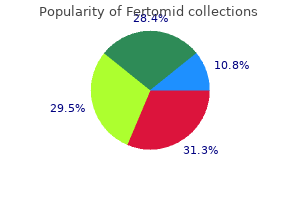
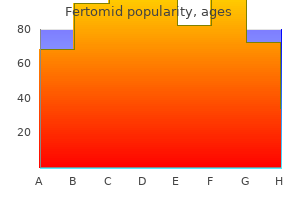
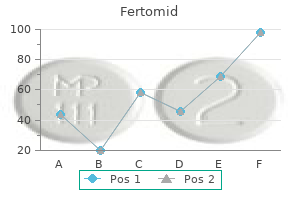
Fertomid dosages: 50 mg
Fertomid packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Fertomid 50 mg buy amex
E (S&F ch39) Pregnancy is related to an alteration in bile composition and increased size of the bile acid pool menstrual cycle at age 7 50 mg fertomid purchase overnight delivery, which would result in breast cancer volleyball socks purchase fertomid 50 mg with visa higher residual gallbladder volumes. Progesterone has a direct inhibitory impact on gut easy muscle tissue, resulting in slow motility and extended intestinal transit time. Treatment with tenofovir within the third trimester of being pregnant is protected and effective in preventing vertical hepatitis B viral transmission. Phenothiazines and vitamin B6 have been proven to scale back symptoms in those that failed initial pharmacotherapy. D (S&F ch39) Methotrexate is a category X treatment and could probably be used with caution in sufferers throughout childbearing age. The optimum period to abstain from this medicine earlier than conception is unknown, however a minimal of 6 months is beneficial. This can differentiate between peritoneal carcinomatosis and tuberculosis peritonitis. Cytology shall be optimistic in more than 90% of the cases of peritoneal carcinomatosis. Secondary bacterial peritonitis usually is polymicrobial and is related to excessive neutrophil counts in ascites fluid. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy usually presents with gentle jaundice (bilirubin <5 mg/dL) and elevated serum bile acids. Laboratory blood work could show evidence of increased serum aminotransferase levels, fragmented pink blood cells on blood smears, as well as decreased platelet counts. Abdominal imaging may be useful in making the analysis by displaying evidence of intrahepatic hemorrhage and infarction. This situation must be suspected in a pregnant patient who current with stomach pain, distension, and cardiovascular collapse. C (S&F ch39) Progesterone instantly inhibits gut smooth muscle tissue and results in slower motility. Maternal alkaline phosphatase levels are normally elevated during the third trimester, largely because of placental production. C (S&F ch40) Radiation enteritis could lead to fibrosis and narrowing of the intestinal lumen as a outcome of stricture formation. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth may be seen in sufferers who underwent radiation because of dilated loops and stasis proximal to stricture. A trial of antibiotics is recommended to treat small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and to control diarrhea. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and subcutaneous octreotide therapy may reduce risk of acute and continual radiation enteritis. D (S&F ch40) Combining chemotherapy with radiation will increase the chance of radiation-induced injury. Other threat factors embrace skinny sufferers (possibly as a result of the bigger quantity of bowel within the pelvis); vasculopathy in sufferers with comorbid conditions, such as historical past of diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, hypertension, and heart problems; in addition to a historical past of collagen vascular illness. Radiation treatment within the susceptible place with external compression is related to much less toxicity probably due to exclusion of small bowel from the radiation area. Additionally, radiation dose and volume of the bowel exposed to radiation are essential determinants of the severity of radiation-induced toxicity. D (S&F ch40) this affected person has radiation colitis with telangiectasias famous on endoscopy. Coagulation methods, such as argon plasma coagulation, are useful for the treatment of bleeding secondary to radiationinduced colorectal ulcerations. Glucocorticoid suppositories can be useful for radiation proctitis and could be thought of for longterm administration. Prostaglandins suppositories corresponding to misoprostol have been investigated as potential radio protective brokers. Similarly, short-chain fatty acids and amino acids, which nourish and defend the colonic mucosa, may be probably protective towards radiation-induced harm. Sucralfate enemas, by forming protecting complexes with rectal mucosae, may alleviate radiation proctitis. D (S&F ch40) the determine shows acute radiation induced esophageal injury with ulcerations and abundant fibroblasts. Amifostine is a free-radical scavenger and has been found to reduce radiation-induced esophageal damage. Glutamine deficiency can happen within the setting of hypercatabolic states like most cancers, and its supplementation protects towards oxidative damage to regular mucosa throughout radiation. Both amifostine and glutamine have been studies in trials to prevent radiation-induced harm. Combining of chemotherapy and radiation remedy will increase the danger of esophageal toxicity. A (S&F ch40) Irradiation of the intestinal mucosa primarily affects the clonogenic intestinal stem cells throughout the crypts of Lieberkuhn. This leads to a decrease in cellular reserves for the villi and leads to shortened villi and reduce absorptive space. In chronic radiation enteritis, the froth cells invade the intima of the arteriolar partitions and contribute to obstructive vasculopathy. C (S&F ch41) Transgastric drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts requires prophylactic antibiotics to prevent cyst infection. D (S&F ch41) Medication-induced venodilation is normally the purpose for hypotension throughout endoscopy, which is commonly conscious of administration of intravenous fluids. The oropharynx or cervical esophagus is the commonest website of perforation during higher gastroesophageal endoscopy. Other complications of sclerotherapy embody perforation, stricture formation, aspiration, in addition to pericardial and pleural effusions. Methemoglobulinemia and severe anaphylactoid reaction can develop in these receiving topical lidocaine as an area anesthetic. Whenever potential, endoscopic remedy ought to be considered, particularly in small perforations that can be handled with clips. The decision to continue antiplatelet agent will relate to the chance of thromboembolic event. Clopidogrel must be held before a procedure that includes polypectomy because it will increase the danger of bleeding. B (S&F ch41) Post polypectomy syndrome consists of a constellation of indicators and signs, together with fever, abdominal pain with rebound tenderness on examination, and leukocytosis. It sometimes happens 1 to 5 days after a procedure and is best treated with hydration, bowel rest, and broad-spectrum antibiotics. Abdominal imaging ought to be performed to rule out localized perforation if worrisome findings are noted on serial belly examination.
Buy fertomid 50 mg on-line
Less notable symptoms include belly ache women's health big book of abs 4-week exercise plan fertomid 50 mg with amex, vomiting women's health clinic anchorage order fertomid 50 mg free shipping, diarrhea, nausea, and conjunctival injection. Cough could persist for longer intervals, and indication of small airway disturbance is commonly found weeks later. Although most youngsters with influenza recover fully after 3 to 7 days, beforehand wholesome youngsters may show severe symptoms and complications. Reported sequelae of the influenza virus include a wide range of secondary sicknesses. Complications might embrace acute otitis media, neurologic problems (eg, encephalopathy, seizures), myocarditis, pneumonia, bronchiolitis, sepsis, myositis, parotitis, and nephritis. A post-influenza myositis may comply with both influenza A or B, although extra generally the latter. Affected sufferers, normally school-aged boys, usually Chapter 31 � Influenza 355 develop severe calf ache 3 to 4 days into their clinical sickness and refuse to weight bear. Laboratory testing may reveal leukopenia and infrequently thrombocytopenia with blood creatine kinase elevated concentrations in the range of 1,000 to 5,000 U/L. Rhabdomyolysis resulting in renal failure occurs not often, and more generally in girls. Influenza is especially extreme in children with predisposing situations similar to hemoglobinopathies, diabetes mellitus, continual renal disease, malignancy, cardiopulmonary disease, cardiomyopathy, and persistent lung disease, together with bronchopulmonary dysplasia, asthma, cystic fibrosis, and neuromuscular ailments, which affect the accessory muscle tissue of respiration. Mortality secondary to the influenza virus has been reported in children with underlying chronic disease as well as beforehand wholesome children. Invasive secondary infections with group A Streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, or other bacterial pathogens could lead to extreme illness and death. Other laboratory exams, corresponding to a complete blood cell count, are also not necessarily indicated in confirming the analysis of influenza illness. A complete blood cell count or blood tradition, nevertheless, could prove helpful in instances when bacterial superinfection or concomitant bacterial illness is suspected. In sufferers with confirmed illness, it might demonstrate hyperaeration, peribronchial thickening, diffuse interstitial infiltrates, or bronchopneumonia in extreme cases. Enlarged hilar lymph nodes and pleural effusion are uncommon in uncomplicated influenza. A excessive index of suspicion for the diagnosis is influenced by the seasonality of influenza. Influenza testing ought to be carried out in any of the following populations: � Patients hospitalized with suspected influenza � Patients for whom a diagnosis of influenza will warrant adjustments in clinical care (Box 31-1) � Treatment of close contacts of patients who died of an unspecified acute illness in which influenza was suspected Respiratory tract specimens must be collected shortly after illness onset, preferably inside the first 72 hours of illness. Specimen collection after 5 days of illness onset may result in false-negative results due to a marked decrease in quantity of viral shedding over time. Optimal specimens in infants and younger kids include nasal aspirates and swabs. Oropharyngeal and sputum specimens result in a lower yield for influenza virus detection. In sufferers undergoing mechanical ventilation, higher and decrease respiratory tract samples must be obtained. Lower respiratory tract samples include endotracheal aspirates and bronchoalveolar lavage. Specimens of nasopharyngeal secretions obtained by swab, aspirate, or wash must be positioned in applicable transport media for culture. After inoculation into eggs or cell culture, influenza virus often may be isolated within 2 to 6 days. Clinical benefit is best when therapy is initiated inside forty eight hours of onset of symptoms. Influenza testing strategies are various, and the particulars of a given medical scenario will dictate which kind of influenza take a look at is the best suited choice. Each technique of testing has its own advantages and disadvantages, as described in Table 31-1. It is crucial to use medical judgment in deciding whether any affected person with an influenza-like sickness should be handled no matter take a look at results, particularly because of the poor sensitivity of speedy influenza diagnostic testing. Confirmatory testing (viral culture or reverse transcriptasepolymerase chain reaction) should be thought of in these cases to affirm accurate results. Clinical judgment is a vital factor in treatment selections for pediatric sufferers presenting with influenza-like sickness. Earlier treatment supplies extra optimum clinical responses, although therapy after forty eight hours of signs within the youngster with reasonable to extreme illness or progressive disease should still provide some benefit. Treatment must be discontinued roughly 24 to 48 hours after symptoms resolve. Antipyretic brokers for control of fever are of critical importance in young kids, because fever and other symptoms of influenza could exacerbate underlying continual conditions. In the United States, 2 classes of antivirals presently are available for therapy or prophylaxis of influenza: adamantanes (amantadine and rimantadine) and neuraminidase inhibitors (oseltamivir and zanamivir). Circulating influenza A viruses proceed to have extraordinarily excessive ranges of resistance to adamantanes, and influenza B viruses are intrinsically proof against adamantanes. Since January 2006, neuraminidase inhibitors (eg, oseltamivir, zanamivir) have been the only really helpful influenza antivirals due to this widespread resistance to the adamantanes and activity of neuraminidase inhibitors in opposition to influenza A and B viruses. A 5-day course of antiviral remedy has been studied and deemed an efficient time course of therapy (Table 31-2). Recommended Dosage and Schedule of Influenza Antivirals for Treatment and Chemoprophylaxis for the 2016�2017 Influenza Season: United States Medication Oseltamivira Adults Children 12 mo Body weight 15 kg 16�23 kg 24�40 kg forty one kg Infants 9 mo�<12 mob Term infants 0�<9 mob 30 mg twice day by day 45 mg twice daily 60 mg twice daily seventy five mg twice daily three. For the 6-mg/mL suspension, a 30-mg dose is given with 5 mL of oral suspension; a 45-mg dose, 7. If the commercially manufactured oral suspension is unavailable, a suspension may be compounded by retail pharmacies (final focus: also 6 mg/mL), based on directions that are current in the package deal label. In sufferers with renal insufficiency, the dose should be adjusted on the premise of creatinine clearance. For treatment of patients with creatinine clearance 10�30 mL/min: seventy five mg once every day for five d. For chemoprophylaxis of sufferers with creatinine clearance 10�30 mL/min: 30 mg as soon as every day for 10 d after publicity or 75 mg once each other day for 10 d after exposure (5 doses). Given its identified security profile, oseltamivir can be used to treat influenza in both time period and preterm infants from delivery. The weight-based dosing advice for preterm infants is decrease than for time period infants. Preterm infants may have lower clearance of oseltamivir due to immature renal perform, and doses recommended for time period infants could lead to very excessive drug concentrations on this age group. Limited knowledge from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Collaborative Antiviral Study Group present the premise for dosing preterm infants using their postmenstrual age (gestational age + chronologic age): 1. Oseltamivir pharmacokinetics, dosing, and resistance among youngsters aged <2 years with influenza.
Order 50 mg fertomid with amex
If the affected person feels ache during the later stages of the appointment menstrual massage order fertomid 50 mg with amex, repeat the buccal infiltration with 1 menstruation kolik generic fertomid 50 mg overnight delivery. Each clinician might want to experiment to see which anesthetic answer (3% mepivacaine or 2% lidocaine with epinephrine) works finest in his or her palms. Pulpal anesthesia must be efficient for roughly 30 minutes with 3% mepivacaine13 and 60 minutes with 2% lidocaine with 1:one hundred,000 epinephrine. On the uncommon occasion that the tooth responds to cold refrigerant after the preliminary intraosseous injection, repeat the injection with 1. Pulpal anesthesia must be efficient for 30 to 60 minutes depending on the solution used. If the affected person feels pain in the course of the appointment, repeat the intraosseous injection. No response Proceed with therapy Alternative choice for supplemental anesthesia Although not as efficacious as intraosseous anesthesia, intraligamentary anesthesia may be given on the mesial and distal side of the tooth utilizing 2% lidocaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine. Remember, the intraligamentary injection could solely be effective for 10 to 20 minutes. Anesthetic failure will occur round 17% of the time in second molars (see Table 2-1). You might wait a few extra minutes after which take a look at the tooth with cold refrigerant; some patients have slow onset of pulpal anesthesia (12% of the time in second molars) (see Table 2-2). When supplemental anesthesia is required A buccal infiltration of 4% articaine with epinephrine of the second molar may be used however may not be totally profitable. This routine should work the overwhelming majority of the time in anesthetizing the second molar. Although uncommon, if the affected person responds to cold refrigerant testing, repeat the intraosseous injection with 1. Once the lip is numb (soft tissue anesthesia is required in the mandible for achievement of the supplemental injections), take a look at the tooth with chilly refrigerant. Anesthetic failure will occur from 19% to 21% of the time in premolars (see Table 2-1). You could wait a couple of additional minutes and then check the tooth with cold refrigerant; some sufferers have sluggish onset of pulpal anesthesia (19% to 20% of the time in premolars) (see Table 2-2). Wait 5 minutes (onset of pulpal anesthesia for a buccal infiltration of articaine is around 5 minutes),10 and retest the tooth with chilly refrigerant. If the affected person experiences ache in the latter phases of the appointment, readminister 4% articaine with 1:one hundred,000 epinephrine. No response Proceed with remedy No response Proceed with treatment tion in the premolars if the perforation website is in hooked up gingiva. If the patient experiences pain in the latter stages of the appointment, readminister the intraosseous injection. A gradual injection (at least 60 seconds) will be less painful and can increase the success fee. Wait 14 to 19 minutes as a end result of onset of pulpal anesthesia is longer for the anterior tooth than the posterior tooth (see Table 2-2). Anesthetic failure will occur 32%, 44%, and 58% of the time in canines, lateral incisors, and central incisors, respectively (see Table 2-1). You might wait a few extra minutes and then take a look at the tooth with chilly refrigerant; some patients have sluggish onset of pulpal anesthesia (16% to 20% of the time in anterior teeth) (see Table 2-2). On the rare event that the affected person responds to the chilly, add an intraosseous injection of 1. Slowly administer an infiltration using a cartridge of 2% lidocaine with 1:50,000 epinephrine or 1:100,000 epinephrine. The greater concentration of epinephrine (1:50,000) will provide a more practical length. This routine should work the majority of the time in initially anesthetizing the maxillary anterior teeth. Duration of pulpal anesthesia It is necessary to realize that pulpal anesthesia starts to decline around half-hour after an preliminary infiltration in maxillary tooth (see Table 3-3). The extra infiltration will delay pulpal anesthesia until no much less than the sixtieth minute. If the intraosseous injection is given, there could also be a need for an additional intraosseous injection, using 1. This routine ought to work nearly all of the time in initially anesthetizing the maxillary premolars and molars. In the rare instance that the tooth nonetheless responds to chilly refrigerant, administer supplemental anesthesia. Duration of pulpal anesthesia In maxillary premolars and molars, pulpal anesthesia starts to decline around 45 minutes after an initial infiltration and at a slower price than in anterior enamel (see Table 3-3). Therefore, if the affected person starts to feel ache (or cold refrigerant testing reveals that the affected person is now not anesthetized) around forty five minutes, an infiltration of 1. Reinjection of a cartridge of 2% lidocaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine should present pulpal anesthesia for 60 minutes. If the tooth is a maxillary second molar, a mesial intraosseous injection site is chosen. If the affected person needs to scale back soft tissue numbness, an injection of phentolamine mesylate (OraVerse) is run utilizing the identical location and same technique (only infiltration site) and in the identical proportion (1:1) as was used initially for the native anesthetic injection. The methods are pretty easy, and with somewhat follow the supplemental strategies could be mastered. The results of a 2-stage injection method on inferior alveolar nerve block injection pain. The wand versus traditional injection for mandibular nerve block in children and adolescents: Perceived ache and time of onset. Articaine buccal infiltration enhances the effectiveness of lidocaine inferior alveolar nerve block. The efficacy of a repeated buccal infiltration of articaine in prolonging duration of pulpal anesthesia within the mandibular first molar. Anesthetic efficacy of the intraosseous injection after an inferior alveolar nerve block. An analysis of the incisive nerve block and combination inferior alveolar and incisive nerve blocks in mandibular anesthesia. The efficacy of a repeated infiltration in prolonging duration of pulpal anesthesia in maxillary lateral incisors. Clinical Factors and Methods Related to Confirming Pulpal Anesthesia Lip numbness A conventional method to affirm anesthesia often involves questioning sufferers if their lip is numb. Soft tissue testing Although gentle tissue testing with a sharp explorer has a high incidence of success (90% to 100%),11�14 pulpal anesthesia will not be current.
Fertomid 50 mg purchase free shipping
It is self-resolving women's health clinic yorkton trusted fertomid 50 mg, never fatal women's health clinic upland ca 50 mg fertomid buy mastercard, and more likely to be related to infections than medicines. The reaction usually happens 1 to four weeks after initiation of the offending medicine. Following the onset of erythema, superficial bullae and erosions develop inside 24 to 48 hours. The original study by Bastuji-Garin included pediatric and adult sufferers, and further research have verified its validity in the pediatric population. Both entities can current with ulceration of the mucous membranes and hemorrhagic crusting of the lips. Clinical Features Patients often current with a prodrome of fever, sore throat, and eye discomfort several days earlier than onset of the rash. Normal-appearing but concerned epidermis may be sheared away by mild lateral strain (ie, Nikolsky sign). Eruption usually starts on the central trunk and then spreads onto the face and extremities. Symptoms of mucosal involvement embrace eye irritation, painful swallowing, or urination and diarrhea. Pathology will show necrotic keratinocytes at all levels of the dermis progressing to full-thickness epidermal necrosis and dermoepidermal separation. Basic chemistries, including serum urea nitrogen, creatinine, liver function studies, and complete blood cell rely, should be obtained. The most necessary first step is a search for and withdrawal of any attainable offending medicine (typically recognized in 77%�95% of cases). Withdrawal of the offending medication can dramatically reduce the risk of mortality, especially in medicine with quick half-lives. Subsequent exposures can result in a extra dramatic and deadly recurrence of this drug reaction. There are few massive studies of both therapy and even fewer within the pediatric population. A review of the available knowledge in kids was published by Del Pozzo and colleagues. There was no clinically vital distinction within the outcomes of the 2 remedy groups, but each had been significantly better than the supportive care groups. Systemic steroid teams have been handled with either prednisone or prednisolone (1 mg/kg/day) or methylprednisolone (4 mg/kg/day) for 5 to 7 days. A systematic evaluate of remedy of drug-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome and poisonous epidermal necrolysis in children. The diagnosis is usually made on scientific examination based mostly on the attribute features (molluscum contagiosum: umbilicated, 1- to 3-mm pearly pink to tan papules; warts: tough, pink to tan, xerotic skin in 1 mm to 1 cm papules). Multiple lesions are notable in immunocompromised hosts, and particular therapies have variable response. Genital warts require specific evaluation because they might symbolize sexual abuse in young youngsters and can predispose to genital cancers. Warts are ubiquitous in the human inhabitants and infrequently seen in youngsters and adolescents, affecting roughly 1 out of 10 people. While warts are typically benign, they carry vital comorbidities, together with psychosocial trauma from visual stigma, ache, and potential bleeding if the lesions are traumatized or develop in sensitive areas. Treatment of warts is primarily geared towards destruction of the contaminated skin cells by quite lots of potential modalities versus lively nonintervention. There are typically four different varieties of warts, together with verruca vulgaris, verruca plantaris, verruca plana, and condyloma acuminatum (Box 58-1). Their names are based on their commonality, location, and sometimes scientific appearance. The virus is well established within the human inhabitants, making warts commonplace in any medical care practice. Occasionally, traumatized warts can resemble pyogenic granulomas due to their red appearance and tendency to bleed (though not as severe). Clinical Features Warts are commonly present in areas of seen trauma or even areas of the physique that bear repetitive microtrauma. Hands, elbows, knees, and ft are a few of the most typical areas the place common warts can be found. If a solitary wart is scratched by way of with a fingernail, the wart can spread, forming a number of warts in a linear configuration matching the scratched sample. Patients with dry pores and skin (ie, xerosis) or an underlying skin illness affecting skin barrier perform (ie, atopic dermatitis) are at a better threat for creating warts. Frequent intentional traumatization, similar to choosing of warts, additionally contributes to their risk of spreading, often to alternate body websites, and ought to be discouraged. Chapter 58 � Warts and Molluscum Contagiosum 633 If warts are traumatized or injured, bleeding could be fairly frequent. Capillaries in the upper papillary dermis are more prominent within the warts and thus more prone to trauma or bleeding. Periungual or plantar warts can simply kind painful fissures and make easy tasks, corresponding to writing or strolling, uncomfortable. Exophytic lesions that protrude from the pores and skin can rub on exterior clothing or objects (eg, jewelry), inflicting irritation or discomfort. The visibility and look of warts can cause some psychosocial issues, particularly lesions on the face or hands/fingers. Verruca Vulgaris (Common Wart) Verrucae vulgaris, or common warts, typically present as raised, xerotic, spherical, skin-colored to pink papules with a tough or "warty" texture to the surface. They can range in size from 1 to 2 mm to several centimeters in diameter, particularly if multiple lesions coalesce collectively. Warts can easily bleed if picked or traumatized, as evidenced by their characteristic thrombosed capillaries that seem as small black macules (resembling "pepper spots"). Common warts may be found in the perineum, buttocks, and, hardly ever, genitalia, which usually have a main supply some place else on the physique. Periungual (around the fingernail) warts typically occur in sufferers who chew their nails or choose the encircling pores and skin. Filiform warts are an exophytic variant of verrucae vulgaris that generally occur on the face, nose, neck, and, not often, trunk. Filiform warts are 1 to 3 mm in diameter and skin coloured and have a skinny exophytic papular stalk with tough fingerlike verrucous projections that resemble the crown of a pineapple. Filiform warts are commonly mistaken for acrochordons (also often recognized as fibroepithelial polyps or pores and skin tags) and can be distinguished with the help of a magnifying glass. Plantar warts can be a few millimeters to centimeters in measurement, solitary or a number of. Lesions are less raised than frequent warts and often have an endophytic look, typically flush with the skin. Thrombosed capillaries are commonly current in plantar warts, a helpful medical sign. Plantar warts have a desire for weight-bearing surfaces and can be fairly painful in consequence, akin to strolling on a small stone.
Proven 50 mg fertomid
Acute otitis media Hyperemia of mucosal lining of mastoid air cells Transudation and exudation of fluid inside mastoid air cells Mastoid periosteitis Loss of bony septae with coalescence into abscess cavity: osteitis and subperiosteal abscess Extension of irritation to contiguous areas 393 35 menstruation questions answers fertomid 50 mg buy mastercard. Initial symptoms often embody pyrexia menstruation 100 years ago fertomid 50 mg discount without prescription, speedy onset of otalgia, excessive crying, irritability, and poor feeding in the toddler. Otorrhea could comply with on rup ture of the tympanic membrane and this usually leads to a reduction in related otalgia. Both viruses and micro organism have been implicated; frequent causative micro organism embody Haemophilus influenzae, S. The phenomenon of accelerating antibiotic resistance of many species of bacteria, especially if the affected person fails to reply after 48 hours of remedy, should be stored in mind. Note that the left pinna is displaced laterally and anteriorly (after allowance for rotation of the image). Typical symptoms or signs of mastoiditis could also be absent, with the patient complaining of continuous otalgia and fever. A high index of suspicion is subsequently required to establish and handle this situation appropriately. Differential diagnosis of a lump behind the ear includes lymphadenopathy and quite a lot of skin lesions similar to sebaceous cysts. History and examination will usually help pinpoint the exact cause, and imaging may be useful in cases of diagnostic uncertainty. Resolution might happen if the infection drains from the mastoid cells via the natural antrum into the tympanic cavity and down the Eustachian tube. Complications could occur if the infection drains onto the mastoid surface, petrous apex, or intracranial spaces. In this latter course, other temporal bone constructions or nearby structures, such as the facial nerve, labyrinth, and venous sinuses, may turn into involved. If these issues are present, multidisciplinary management with neu rologists, neurosurgeons, pediatricians, microbiologists, radiologists, and intensive care specialists is regularly required. Intracranial Meningitis Commonest intracranial complication, typically in young children, but also these with congenital inner ear abnormality or cochlear implants. If mastoid surgical procedure is needed, this may be greatest delayed until medical remedy of meningitis takes effect. Abscess/empyema Extradural abscess is second commonest intracranial complication, typically related to persistent ear disease; surgical drainage required. Subdural empyema is uncommon, with patients having further meningeal irritation, focal neurological signs, or seizures. Brain abscesses are extra widespread with chronic disease; neurosurgical drainage may be required although some resolve with intravenous antibiotics. Sigmoid sinus thrombosis Due to erosion of bone over sinus, with formation of infected thrombus that can propagate or embolize; septicemia and swinging pyrexia may happen. Extent of surgical management is controversial, and will include myringotomy with air flow tube in choose cases, or cortical mastoidectomy with or without needling of sinus and thrombus removal. Labyrinthitis Serous labyrinthitis usually results in full recovery, however in suppurative labyrinthitis with pus formation the listening to loss and vestibular impairment could additionally be everlasting. Recommended therapy contains intravenous antibiotics and a variety of mastoidectomy. Severe headache Photophobia Neck stiffness Cranial nerve palsies Focal neurological indicators Persistent of swinging pyrexia Sepsis Meningeal irritation Failure to respond to preliminary antibiotic remedy 35. Identification of responsible micro organism could also be possible via blood cultures, ear discharge swabs, or microbiological diag nosis of intraoperative specimens. Certainly myringotomy for microbiological prognosis is suitable if uncommon micro organism are suspected such as in immunocompromised patients. Some also advocate cortical mastoidectomy in these cases, however whether this is warranted is unclear. Once a subperiosteal abscess has developed, myringotomy with air flow tube insertion ought to be mixed with abscess drainage. There are several problems confronting the surgeon who wished to do a full cortical mastoidectomy on this state of affairs. In many youngsters, the abscess itself will already have destroyed the outer bony cortex, and the exuberant granulation tissue within the mastoid air cells makes identification of formal landmarks tough. The selection of antibiotic ought to be guided by native pathogens and resistance patterns. Duration of remedy should be guided by clinical response, with different papers recommending differ ent antibiotic durations, ranging from 5 to 14 days intra venous use, and from 5 days to four weeks of further oral antibiotic use. Augmentin would be a suitable empiric oral antibiotic selection if no particular pathogen is isolated. Some advocate myringotomy with aspiration of fluid for microbiology in all circumstances, but as Flowchart 35. For these causes, many surgeons argue that straightforward abscess incision is appropriate for most such circumstances. Acute mastoiditis in kids: a 10year retrospective and validated multicenter examine. Acute mastoidi tis: enhance of incidence and controversies in antibiotic treat ment. Effect of antibiotics for otitis media on mastoiditis in kids: a retrospective cohort examine using the United kingdom common practice analysis database. Infection progresses from inflammation within the center ear and mastoid air cells, spreading to periostitis, osteitis, and subperiosteal abscess formation. Children should be admitted and management with intravenous antibiotics instituted. If this administration fails, or subperiosteal abscess is pre despatched, surgical procedure is required; myringotomy and air flow tube insertion are useful, as is easy abscess incision, and cortical mastoidectomy may be warranted in some. Thorough anatomical knowledge together with perceive ing of the different pediatric anatomy is necessary when undertaking surgical procedure. Pitfalls � To keep away from under- or overestimation of measurement, the dimensions must be measured with some form of ruler. This chapter not only outlines the strategy to the kid with a neck lump, specializing in lymphadenopathy and salivary gland lesions but also provides a brief description of the varied differential diagnoses. Neck lumps in youngsters are most likely inflammatory in nature, with cervical lymphadenopathy as the commonest pathology. Though the incidence of malignancy is low, the top and neck is concerned in 12% of childhood malignancies. Location of the lump is a vital feature to decide on examination, as is lump mobility and any skin adjustments. A search for a attainable supply of infection (including oropharynx, mouth, ears, and scalp), and different lymph nodes must be made. Lump dimension should be measured with some type of ruler, as approximation can either underestimate or overestimate the actual measurement, since measurement of progress over time can assist in deciding intervention. There may be a couple of site concerned, and this can have implications for deeper lesions.
Syndromes
- Breathing tube
- Phenacemide
- Vomiting (may contain blood)
- Hair loss
- A foul odor from the ulcer
- Platelet aggregation test
- Developmental milestones record - 3 years
- Blood glucose test
- Turning blue
Fertomid 50 mg buy discount on-line
The scientific options of acute encephalitis overlap with acute meningitis- sufferers with either syndrome could present with fever pregnancy yoga 50 mg fertomid purchase overnight delivery, headache women's health center worcester ma order fertomid 50 mg overnight delivery, and altered psychological status-and both diagnoses have to be thought of. Encephalitis additionally needs to be distinguished from encephalopathy (eg, secondary to metabolic problems, hypoxia, ischemia, medication, toxins, or systemic infection), which is defined by a disruption of brain perform in the absence of direct irritation of the mind parenchyma. The absence of fever, a more gradual 290 Succinct Pediatrics onset of symptoms, and lack of pleocytosis or absence of focal changes on mind imaging can normally differentiate metabolic and poisonous causes of encephalopathy from encephalitis. Clinical Features Pathogenicity of the etiologic agent, severity of involvement, anatomic localization of affected parts of the nervous system, and immune reaction of the host all act to determine the medical findings. Diffuse neurologic involvement can present with behavioral or personality modifications, decreased consciousness, and generalized seizures. Focal seizures, hemiparesis, motion problems, ataxia (ie, rhombencephalitis), and cranial nerve defects (ie, rhombencephalitis) are evidence of localized involvement. Limbic encephalitis signs embody memory loss, temporal lobe seizures, movement disorders, and affective or psychiatric findings. Limbic encephalitis in adults is commonly a paraneoplastic course of with autoantibodies, but in youngsters and adolescents, tumors are less frequent. The initial manifestations of encephalitis usually resemble an acute systemic sickness with fever, headache, or irritability. Table 27-1 lists epidemiologic threat components, and Table 27-2 medical findings associated with specific etiologies. Diagnosis Early identification of the etiology can have a serious impact on both administration and prognosis. In addition, identification of a selected etiologic agent, if possible, is important for potential prophylaxis, counseling of sufferers and households, and public well being interventions. After initial stabilization of the cardiorespiratory status and control of any seizure exercise, the analysis ought to embody a radical historical past and bodily examination, initial laboratory exams, lumbar puncture, neuroimaging, and electroencephalography. The historical past and physical examinations can provide necessary epidemiologic clues in establishing the analysis. Often the affected person is unable to answer questions because of age or altered consciousness, and the information must be obtained from mother and father, caregivers, or relations. Prevalence of illness in the local people, ill contacts, journey history, social historical past, recreational actions (eg, freshwater swimming), toxin publicity, insect or animal contacts, vaccination history and timing, and historical past of current infectious illness may help elucidate the trigger. The physical examination ought to embody a careful neurologic examination including mental standing, motor, sensory, cranial nerve, cerebellar, and reflex Chapter 27 � Encephalitis 291 Table 27-1. Possible Etiologies of Encephalitis Based on Epidemiology and Risk Factors Risk Factor Neonate Agammaglobulinemia Animal contact Bats Cats Raccoons Rodents Sheep and goats Skunks Immunocompromised Ingestion gadgets Raw or partially cooked meat Unpasteurized milk Insect contact Mosquitoes West Nile virus, St. The management of encephalitis: clinical apply tips by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Other parts of the physical examination can counsel an etiologic agent, corresponding to vesicular or maculopapular rash, lesions of hand-foot-and-mouth illness, and rash of Rocky Mountain noticed fever. Laboratory and neuroimaging evaluations can also present clues to the etiology and support the medical prognosis. Certain laboratory exams must be accomplished on all sufferers with suspected encephalitis, however other tests are indicated provided that there are constant medical or epidemiologic findings (eg, geographic location, season, exposure). Box 27-3 outlines the preliminary diagnostic evaluation for sufferers with encephalitis. This is usually carried out after neuroimaging to rule out mass lesion or shift in intracranial structures if indicated. Cerebrospinal fluid indices in sufferers with viral encephalitis can be much like these in sufferers with viral meningitis and meningoencephalitis and overlap with bacterial meningitis. Red blood cells are often absent, and protein concentration is often elevated. Sedation for neuroimaging could also be contraindicated, so think about contacting an anesthesiologist for common anesthetic if needed. It could have a limited role and must be considered in circumstances of encephalitis of unknown etiology that deteriorate despite therapy with acyclovir. Chapter 27 � Encephalitis 295 established solely by brain biopsy, but this has turn into unusual with the routine use of magnetic resonance imaging and availability of diagnostic polymerase chain response and antibody assays. Management Encephalitis can be an acute life-threatening emergency that requires immediate intervention. Depending on how severely the patient is affected, intensive care could also be required. Focus of the preliminary evaluation and management ought to be on treatable and customary causes of encephalitis in addition to supportive care. Box 27-4 lists the treatable or probably treatable infectious and noninfectious causes of acute encephalitis-like syndromes. Rapid evaluation and administration of elevated intracranial stress is crucial to scale back cerebral edema, diminish cerebral anoxia, and reduce secondary brain harm. It is essential to anticipate and be prepared for issues corresponding to hyperthermia, inadequate respiratory change, fluid and electrolyte imbalance, aspiration and asphyxia, abrupt cardiac and respiratory arrest of central origin, cardiac decompensation, and gastrointestinal bleeding. Patients must be positioned in acceptable an infection control� based mostly isolation precautions according to scientific and epidemiologic info. If Listeria infection is suspected, the addition of ampicillin should be thought of. Other empiric therapy could additionally be indicated for other infectious causes of encephalitis suspected on the basis of scientific or epidemiologic info. Following the identification of a particular etiologic agent or noninfectious cause in a patient with encephalitis, appropriate antimicrobial therapy or other administration ought to be initiated. Immunotherapy (corticosteroids, intravenous immune globulin, plasma change, or a mix of those) and elimination of the tumor, if current, has been related to improved consequence. Suggested preliminary therapies for selected brokers that trigger encephalitis are introduced in Table 27-3. Outcome and Long-term Monitoring There are limited data on the long-term outcomes in kids with encephalitis. Effects on the central nervous system could include intellectual, motor, psychiatric, epileptic, visible, or auditory sequelae. The short- and long-term outcomes rely partially on the etiologic agent, findings at the time of presentation, and age of the child. Rabies and Naegleria fowleri, for example, are known to have virtually one hundred pc mortality. Coma, convulsions, intensive care, or focal neurologic findings in the early part of encephalitis are related to worse outcomes. Herpes simplex Chapter 27 � Encephalitis 299 virus encephalitis is one of the best studied and has a worse prognosis for survival and residual morbidity than enteroviruses. Once the affected person is discharged from the hospital, monitoring should continue for no less than 1 12 months, including supportive care and rehabilitation, the extent of which is determined by neurologic debility.
Purchase fertomid 50 mg mastercard
Predictable summer�early fall outbreaks of such infections are normally caused by members of the Picornaviridae family and echoviruses breast cancer 2nd stage survival rate cheap fertomid 50 mg otc. Unusual causes of meningitis include Baylisascaris procyonis (raccoon roundworm) and fungal pathogens women's health center of grants pass fertomid 50 mg buy discount on line, together with endemic mycoses and Aspergillus species. Autoimmune ailments (eg, lupus), drug reactions (eg, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole), and malignancies (eg, leukemia, lymphoma) could cause aseptic meningitis. Tick-borne rickettsial infections (Rocky Mountain spotted fever and ehrlichiosis) may be associated with encephalopathy and pleocytosis, and testing may not acutely affirm this prognosis. Many illnesses mimic meningitis, and these must be considered when formulating a differential diagnosis. Patients with fever and nuchal rigidity might have a retropharyngeal abscess, whereas the patient with febrile seizure may have Human herpesvirus 6 infection. Clinical Features Classic indicators and symptoms of meningitis embody headache, fever, photophobia, and nuchal rigidity; nevertheless, this can be very necessary to observe that medical options range depending on age and infecting organism. Younger pediatric sufferers might not demonstrate classic symptoms, like nuchal rigidity (Table 4-1). Especially in young infants, medical manifestations of bacterial meningitis are variable and nonspecific, and clinicians ought to know that no single signal is pathognomonic. When obtaining the history of present sickness, parental reporting of lethargy, irritability, tremor or twitching, poor feeding, apnea, or vomiting ought to increase medical concern for meningitis. Other findings in the age group that may point out meningeal inflammation embody paradoxic irritability with the infant showing more irritable when held and most snug when left flat, extended, and immobile. Additionally, any neonate presenting with a sepsis-like image needs to be evaluated for meningitis. As with the neonatal population, presentation with a sepsis-like image, fifty six Succinct Pediatrics Table 4-1. Physical examination findings ought to look for traditional indicators of meningeal irritation that can be elicited with testing for Kernig and Brudzinski signs. Kerning signal is optimistic when a affected person mendacity supine whose thigh is flexed at a right angle to the trunk has ache with knee extension. Brudzinski sign is optimistic when the patient flexes the knees or lower extremities on passive flexion of the neck. Other physical examination findings to contemplate embrace cranial nerve palsies in sufferers with Lyme disease�caused meningitis and skin manifestations like purpura which might be traditional for meningococcal infection. Patients with viral meningitis have scientific indicators and symptoms which are much like bacterial meningitis however are usually much less extreme. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis should include measurement of pressure, purple and white blood cell counts with differential, glucose concentration, and protein measurements, in addition to Gram stain and culture. Bacterial meningitis is usually characterised by pleocytosis with a polymorphic nuclear cell predominance. Blood cultures are sometimes positive for the same offending organism, particularly in younger patients/neonates. Glucose and protein concentrations are usually regular, and Gram stain will stay negative. Culture and Gram stain results are the only reliable laboratory indicator on this setting. With sure pathogens, particularly N meningitidis, this can occur as rapidly as 1 hour after the primary dose. For patients with traditional laboratory finding of meningitis and a unfavorable culture following pretreatment, discussion with an infectious illnesses specialist is really helpful. In the neonatal inhabitants, some practices advocate magnetic resonance imaging close to the end of the treatment course to evaluate for problems for the an infection. Admission to a pediatric intensive care unit must be thought of for patients with cardiorespiratory compromise (ie, respiratory distress or shock), a Glasgow Coma Scale score of less than eight, or signs and signs of elevated intracranial stress or focal neurologic deficits. Some experts suggest that 60 Succinct Pediatrics any child younger than 1 yr with bacterial meningitis be cared for initially in a pediatric intensive care unit, even if apparently clinically stable on admission. Initial antibiotic choices vary, based on age of affected person, to cowl the most probably bacterial organisms. A number of antibiotic therapies are proposed and range by reference considered and clinician preference. A combination of ampicillin (300 mg/kg/day divided every 6 hours) and cefotaxime (200�300 mg/kg/day divided each 6 hours) is enough empiric remedy for suspected meningitis. Acyclovir (60 mg/kg/day each 8 hours) is really helpful in addition to antibiotics till readability in etiology is established. Some clinicians advocate for using acyclovir in all sufferers younger than 30 days presenting with fever and treated with antibiotics for sepsis-like sickness, whereas others recommend its use in sufferers with regarding danger components (ie, pleocytosis, seizures, vesicular rash). Empiric coverage with a third-generation cephalosporin (ceftriaxone a hundred mg/kg/day given as soon as day by day or divided twice every day or cefotaxime 200�300 mg/kg/day divided each 6 hours) plus vancomycin (60 mg/kg/day divided every 6 hours) is really helpful for suspected meningitis. A vancomycin stage of 15 mcg/mL ought to be focused for those with pneumococcal meningitis for which cephalosporin resistance is confirmed. The choice of antibiotics for sufferers with a historical past of anaphylaxis to penicillins or cephalosporins should be mentioned with an infectious diseases Chapter four � Meningitis 61 Suspected Bacterial Meningitis Based on History Rapid Physical Assessment 1. Duration of therapy is dependent upon multiple components, including organism identified, scientific response to remedy, issues, and age of the patient. Consultation with an infectious illnesses specialist is more doubtless to be useful typically. Shorter courses of seven days are thought of acceptable for meningococcal illness, while longer 14-day programs should be thought of for Listeria, group B Streptococcus, and S pneumoniae. For sufferers in whom an enterovirus has been identified and medical improvement is seen, antibiotics therapy could be discontinued. The use of adjunctive corticosteroids ought to be thought of when bacterial meningitis is suspected. In a meta-analysis across all age teams, corticosteroids decreased the speed of severe hearing loss, any hearing loss, and neurologic sequelae. Subgroup analysis revealed a differential impact based mostly on organism, with a discount in severe hearing loss in H influenzae type b meningitis and a lowered mortality in pneumococcal meningitis. Meningitis can current with significant systemic issues, and careful consideration of administration of problems must be prioritized. The prognosis ought to be considered in all patients with bacterial meningitis plus serum sodium values of less than a hundred thirty five mg/dL or within the patient with low urine output. In the hemodynamically stable patient, moderate fluid restriction (80% of normal) and use of isotonic fluid must be considered. Generalized seizures usually occur on presentation or within the first seventy two hours of sickness and replicate irritation to the meninges. Focal seizures typically happen after the Chapter 4 � Meningitis 63 third day of illness and should alert the clinician to a vascular or infectious complication of bacterial meningitis. Long-term Monitoring and Implications Bacterial meningitis has a demise fee as high as 10% with neurologic morbidity the commonest sequela among survivors.
Discount fertomid 50 mg otc
Outbreaks can happen in closed communities menstruation timeline fertomid 50 mg order, similar to army camps contemporary women's health issues for today and the future 4th edition buy fertomid 50 mg, and are often brought on by atypical serotypes not normally related to sepsis or meningitis. Conjunctivitis and Other Rare Presentations Meningococcal conjunctivitis presents as purulent eye discharge with conjunctival injection, eyelid edema, or chemosis. The syndrome is rare and clinically indistinguishable from other causes of bacterial conjunctivitis. The differential diagnosis contains gonococcal illness and colonization with nonpathogenic Neisseria species. In one examine, the time to improvement of systemic meningococcal disease was forty one hours on average (range: 3�96 hours); invasive illness was much more common (19 times) in patients who had received topical therapy alone for conjunctivitis than in those that had received systemic remedy. Other unusual manifestations of meningococcal an infection embody endophthalmitis, neonatal sepsis, and cellulitis. Chapter 18 � Meningococcal Disease 191 Evaluation the clinical presentation of invasive meningococcal disease could be very tough to differentiate from other causes of sepsis or meningitis in kids, so patients are normally handled empirically till the organism is recognized. In most cases of meningococcal sepsis, inflammatory markers are elevated and white blood cell counts are abnormal (ie, high or low). Specimens for tradition should be transported instantly for processing and incubation as a outcome of the organism is fragile in chilly or unfavorable conditions. The organism is quickly killed by antibiotics, so blood culture results collected after antibiotics are almost all the time adverse (>95%). Most samples collected after any intravenous antibiotics are sterile, and 5 hours after antibiotic administration almost all are sterile. Where rash is distinguished, Gram stain and culture of aspirated fluid, pores and skin scrapings, or biopsies from lesions might yield the diagnosis. Meningococci may also be recognized by tradition of samples from other websites, together with synovial fluid, conjunctival discharge, and sputum. The panel includes meningococcus, and may be helpful particularly in culture-negative or pretreated cases. Susceptibility testing is beneficial by some consultants for all meningococcal isolates as resistance to fluoroquinolones, penicillin, and even ceftriaxone has been reported. Resistance to penicillin and ceftriaxone is very rare in the United States but extra common in another international locations. Knowledge of local epidemiology is essential if meningococcal disease happens in a returned traveler. Investigation for Acute Complications In addition to ordinary investigations undertaken for routine administration of sepsis, such as clotting research and arterial or venous strain monitoring as indicated, there are a variety of additional concerns in youngsters with meningococcal illness. Hyponatremia related to syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone can happen in meningitis from any cause and requires careful management to stop mind damage. Daily sodium and fluid balance monitoring may help stop extreme hyponatremia by guiding fluid management. Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome describes adrenocortical dysfunction attributable to bilateral adrenal gland hemorrhage and is an uncommon however essential complication of meningococcal disease and other causes of sepsis. Indications for mind imaging include localizing neurologic signs, coma, hydrocephalus, and persistent fever for greater than 9 days or recurrent fever after initial defervescence. Investigation for Predisposing Conditions Complement deficiency or dysfunction is associated with markedly increased danger for meningococcal disease. Patients with these situations usually have milder illness and a lower probability of dying but an elevated risk of recurrent meningococcal an infection. The threat is highest in those with recurrent illness, older age at presentation (>10 years), or infection with an uncommon serogroup. Positive results ought to immediate education, early empiric remedy for future potential episodes, meningococcal vaccination, and testing of relations. Chapter 18 � Meningococcal Disease 193 X-linked properdin deficiency is related to increased severity of meningococcal illness, with a fatality price of up to 75%. Abnormal outcomes ought to again prompt schooling, early empiric treatment for future potential episodes, meningococcal vaccination, and testing of relations. Patients with fatal illness ought to endure testing for properdin deficiency due to implications for members of the family. Investigations in Recurrent Meningococcal Disease Most stories of recurrent meningococcal illness have identified classical complement pathway abnormalities, but various pathway abnormalities additionally happen. Management the first priority in management of bacterial sepsis is supportive care and treatment of shock. While the kid with fever and purpura is likely to have meningococcemia, purpura fulminans has often been associated with bacterial sepsis caused by different pathogens, including Haemophilus influenzae, group A Streptococcus, S aureus, and S pneumoniae. Thus, empiric therapy of severe bacterial sepsis (with or with out purpura) should include cefotaxime or ceftriaxone plus vancomycin. Vancomycin will not be required in areas the place penicillin-resistant pneumococci and methicillin-resistant S aureus are uncommon. Definitive therapy of bacterial sepsis is based on identification of the organism and susceptibility testing. However, susceptibility testing for meningococci is poorly standardized and the rate of resistance to penicillin or third-generation cephalosporins within the United States is extremely low. Thus, penicillin G, ampicillin, cefotaxime, or ceftriaxone may be used as definitive therapy. Cefotaxime or ceftriaxone is most well-liked for travelers from areas the place penicillin resistance has been reported. As for bacterial sepsis, the first priority for remedy of youngsters with presumed bacterial meningitis is supportive care, correction of hemodynamic instability, and administration of increased intracranial stress in extreme instances. The addition of vancomycin is critical as a end result of pneumococcal sepsis and meningitis can mimic meningococcal infection, and till cultures permit for definitive remedy, vancomycin ought to be included within the empiric regimen. Steroids, activated protein C (now withdrawn from the market), and other potential adjunctive therapies for patients with meningococcemia and different forms of bacterial sepsis have been studied extra extensively in adults than kids, however minimal evidence helps their use. All circumstances of meningococcal illness should be reported to the suitable local or state well being division instantly, and to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention inside 14 days. Droplet isolation should be utilized until 24 hours of acceptable therapy has been offered. Primary Prevention Primary prevention of meningococcal disease is a vital public health objective. Therefore, vaccination of younger children at high risk may be recommended within the near future. Secondary Prevention Close contacts of individuals with invasive meningococcal illness are at threat of subsequent invasive meningococcal disease and will receive chemoprophylaxis. Close contacts include family contacts (and anyone who incessantly slept in the identical dwelling during the 7 days prior to sickness onset), youngster care or preschool contacts at any time through the 7 days before illness onset, anybody with direct publicity to secretions of the index affected person (including mouth-tomouth resuscitation or unprotected contact throughout endotracheal intubation), and passengers seated instantly subsequent to the index affected person throughout airline flights lasting more than eight hours. Prophylaxis should solely be given if the newest contact was throughout the previous 14 days.
50 mg fertomid order with mastercard
Bimanual palpation of the realm women's health partners boca raton fertomid 50 mg buy cheap, palpation to look for salivary move womens health supplements best fertomid 50 mg, and ruler measurement of the lesion assist doc development of the situation. Congenital lesions: Lymphatic malformations, first branchial arch cyst with duplication anomalies and hemangiomas can current in the parotid area. Inflammatory lesions together with viral infections, such as mumps, proceed to happen commonly. Mild pyrexia with painful enlargement of the salivary glands is the most common presentation. Atypical mycobacterial infection of this area must be thought-about in kids beneath age 6 years. A painless dusky pores and skin change of a mass in the parotid or submandibular area is pathognomonic of this condition. Recurrent parotitis of childhood is a rare situation, although the second most common reason for parotid irritation in youngsters after mumps. There is biphasic age distribution with presentation between 2 and 5 years or round 10 years, and most outgrow the condition by 15 years. Patients current with recurrent episodes (mean = 8 per year) of parotid swelling, pain, and fever. Sialendoscopy and intraductal corticosteroid may be effective in reducing recurrence. Salivary gland tumors: It is important to notice that the salivary gland space comprises mesenchymal and epithelial tumors of equal frequency, and whereas 70% of these lesions are benign, 30% are malignant. They are likely to arise from the most important salivary gland area in 80% of instances, particularly within the parotid space. In a survey of 324 salivary gland tumors, 60% were hemangiomas, 27% lymphatic malformations, and 13% had been stable tumors. Of the salivary gland tumors, 60% got here from parotid gland, 18% submandibular gland, 7% palate, 7% buccal mucosa and gingiva, 5% tongue, and 2% lip. Benign tumors such as pleomorphic adenomas account for 30% of pediatric salivary gland tumors and the remedy is similar as in adults, a careful resection with facial nerve preservation. Facial nerve monitoring is essential throughout dissection as the peripheral branches turn out to be miniscule as one goes extra peripheral in the clearance. The incidence of malignant lesions will increase with rising age but most have an excellent prognosis. Mucoepidermoid is the most typical salivary malignancy in youngsters, with acinic cell tumors and adenoid cystic carcinoma much less common. Wide excision is required, and nerve grafting is usually very successful in children. A pediatric oncology group should at all times be concerned within the administration of these circumstances. It originates particularly within the ducts of Rivini inside the gland, or hardly ever, from a minor salivary gland in the same space. Ranulas are categorized into oral or cervical (plunging), depending on their relation to the mylohyoid muscle. They are commonest between ages 10 and 20 years, but may be recognized antenatally. Management of cervical ranulas ought to embrace full surgical excision of the oral part and the Chapter 36: Neck Lump(s) associated salivary gland, with drainage of the cervical part either externally or intraorally. They are nodular sclerosis, combined cellularity, lymphocyte-rich subtype and lymphocyte-depleted subtype. The illness is histologically divided into low, intermediate, and excessive grade and most youngsters present with high-grade tumors. Ninety-percent are mature B cell lymphoma (Burkitt or diffuse giant cell), lymphoblastic lymphoma, or anaplastic massive cell lymphoma. Specimens must be sent recent to allow circulate cytometry, immunohistochemical staining, and molecular genetic testing. Surgical remedy is required only for biopsy, as the main treatment is either chemotherapy or radiotherapy. The presence of cranial nerve palsy and facial pain suggests skull base involvement. Traditionally, chemoradiation is the mainstay of therapy, but advances in endoscopic cranium base and craniofacial surgery might make surgery an important possibility in each primary and recurrent illnesses. Neuroblastoma arises from neural crest cells within the undifferentiated sympathetic nervous system, and its predominant websites are the adrenal gland and the sympathetic chain. The disease typically presents as progressive enlargement of the cervical or supraclavicular lymph nodes, with much less involvement of the axillary and inguinal nodes. Patients additionally present with constitutional symptoms similar to fever, evening sweats, and weight reduction. The prognosis is made by lymph node biopsy and the therapy is carried out with chemotherapy or radiotherapy according to the stage. The appropriate investigations will help choice making and a administration plan can then be recommended. It is essential to consult different disciplines in children with malignancy or other complicated displays. The value of fantastic needle aspiration cytology in the analysis of pediatric head and neck tumours. Fine needle aspiration biopsy: position in prognosis of paediatric head and neck masses. Risk of recurrence in children operated for thyroglossal duct cysts: A systematic review. Ultrasound to differentiate thyroglossal duct cysts and dermoid cysts in children. Individual tradition permits successively evaluating embryo improvement and quality to ease the number of one of the best embryo(s) for transfer. Time-lapse incubators for steady analysis and tradition of embryos at low oxygen. Labelling machine: for creation of patient-specific identification labels for the dishes. Time Course for Preparation of Dishes � In the afternoon of the day of egg collection: Prepare and pre-incubate the culture dishes in a single day for the zygotes. How to Prepare Different Types of Dishes Independent of Culture Strategy � Culture in center-well dishes. Some five-well dishes have a sloped wall, which makes it additionally possible to use for smaller droplets. This could be carried out at the gas provide itself, or more generally with a step-down regulator at the fuel outlet throughout the lab.
Generic fertomid 50 mg mastercard
Chapter 26 � Cytomegalovirus 279 consequence of congenital an infection women's health clinic quivira 50 mg fertomid cheap free shipping, together with cognitive deficits menstrual blood clots fertomid 50 mg order free shipping, cerebral palsy, visual impairment, and, most regularly, sensorineural listening to loss. A sepsis-like syndrome has been described and is characterized by respiratory distress, poor perfusion, and hepatosplenomegaly. Laboratory abnormalities include neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and transaminitis. Cytomegalovirus is the most typical cause of heterophilenegative mononucleosis-like sickness. Hepatosplenomegaly could also be accompanied by elevated transaminase concentrations and elevated direct and indirect bilirubin ranges (see Table 26-1). Cytomegaloviral-specific IgM antibodies are usually detectable within the first 2 weeks following onset of illness, whereas IgG antibodies are often undetectable until 2 to 3 weeks after onset of symptoms. However, IgM antibodies may be detectable for 4 to 6 months after major an infection and may typically be positive with reactivation or reinfection. These assays are based on the remark that IgG antibodies of low avidity are current in the course of the first few months after onset of an infection and take 16 to 20 weeks to mature to high ranges. Intracranial calcifications in a neonate with congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Periventricular calcifications in a neonate with congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Results are primarily based on observation of typical cytopathic impact in cells, which can take 2 to three weeks. The shell vial assay is a extra fast tradition technique that has changed conventional cell culture in many laboratories. Use of the assay is limited in pediatrics, particularly among those with leukopenia, due to the blood volume necessities. Results from these checks can be utilized to decide which preventive technique is most appropriate on the basis of danger stratification. The presence of viremia has been demonstrated to be a predictive issue for improvement of end-organ illness and is used for initiating preemptive therapy earlier than overt disease is established. Urinary or salivary cultures are also unhelpful as a result of isolation of virus could replicate shedding and may not correlate with illness. Cognitive deficits could be predicted by the presence of microcephaly or intracranial calcifications, both of which are associated with average to extreme dysfunction. Treatment is Chapter 26 � Cytomegalovirus 285 individualized on the basis of severity of illness and degree of immunosuppression. Prevention of illness may be completed using either prophylaxis or preemptive therapy, however prophylaxis is usually recommended for pediatric sufferers, especially those at highest risk. Duration of prophylaxis varies by organ sort, threat stratification, and institutional practice, but is often three to 6 months. Patients ought to be monitored for neutropenia and other proof of bone marrow suppression. Although most information on the efficacy of these regimens are primarily based on adult research, the identical methods are typically extrapolated to be used in children. Year 2007 place assertion: ideas and tips for early listening to detection and intervention packages. International consensus tips on the administration of cytomegalovirus in solid organ transplantation. Severe cytomegalovirus infection in apparently immunocompetent sufferers: a systemic evaluate. Further diagnostic testing is determined by epidemiologic factors, scientific presentation and course, and cerebrospinal fluid and magnetic resonance imaging results. Acyclovir must be began in all sufferers, pending results of diagnostic research. Pragmatically, encephalitis is diagnosed in most sufferers on the idea of presence of an inflammatory strategy of the mind in association with scientific proof of neurologic dysfunction. Inflammation of the mind parenchyma may be related to a meningeal reaction, spinal wire irritation (ie, myelitis), or nerve root involvement (eg, radiculitis), by which case the phrases meningoencephalitis, encephalomyelitis, meningoencephalomyelitis, myeloradiculitis, and meningo-encephaloradiculitis are used. Limbic encephalitis refers to encephalitis of the temporal lobes and sometimes of other limbic constructions. Rhombencephalitis refers to encephalitis affecting the hindbrain (ie, brainstem and cerebellum). Causes and Differential Diagnosis Viral infections are the most generally recognized causes of acute encephalitis (Box 27-1). However, even with in depth diagnostic testing, the etiology of encephalitis in most patients is undetermined. Noninfectious ailments (eg, collagen vascular ailments, vasculitis, and paraneoplastic syndromes) can have comparable scientific presentations to infectious causes of encephalitis (Box 27-2). On the basis of the California Encephalitis Project, anti-N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor encephalitis was the main trigger (32 of 79 cases) with enteroviruses identified in 30 patients, Human herpesvirus 1 in 7 patients, and varicella-zoster and West Nile viruses in 5 sufferers each. Monitoring all through childhood ought to embrace developmental assessments regularly because these youngsters are in danger for developmental or mental incapacity. Neuropsychological testing may be helpful as properly, especially when growing an education plan for the kid. Virus and immune-mediated encephalitides: epidemiology, prognosis, treatment, and prevention. The frequency of autoimmune N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor encephalitis surpasses that of particular person viral etiologies in young individuals enrolled within the California encephalitis project. Life-threatening sickness may observe an infection in neonates, and the disease may mimic neonatal herpes simplex virus infection. Those with immunodeficiencies, each humeral and mixed, may present with persistent central nervous system an infection, a dermatomyositis-type sickness, or disseminated an infection. Polymerase chain reaction exams are useful to confirm an infection and will shorten duration of hospitalization for these with meningitis. Most infections brought on by members of the 2 genera occur in children younger than 5 years and, in particular, youthful than 2. Causes and Differential Diagnosis Enteroviral and parechoviral infection in neonates could present similarly and mimic bacterial sepsis or infection caused by herpes simplex virus. In older kids, the exanthema of hand-foot-and-mouth illness (coxsackievirus A16) might mimic chickenpox, herpes simplex virus, or eczema herpeticum. Other causes of cardiac dysfunction must be thought-about, including anatomic lesions (eg, aortic stenosis, anomalous coronary artery) and cardiomyopathies, including metabolic ones (eg, glycogen storage disease). The onset is abrupt with fever in affiliation with any of the following findings alone or together: poor feeding, lethargy, irritability, vomiting, diarrhea, higher respiratory tract signs, or exanthems. Physical findings could additionally be absent or minimal, consisting of gentle pharyngeal and conjunctival injection, lymphadenopathy, and exanthems.
